IAM key attribute reference
AI summary
About AI summaries.
An IAM key authorizes your requests to send or search events in Imply Lumi from a third-party application. When you create a key, you add and configure an integration for the application. These configuration settings are called IAM key attributes. IAM key attributes include default values for event metadata and configuration parameters to parse events.
This topic provides reference information on IAM key attributes. Before continuing, ensure that you have a basic understanding of the event model and IAM keys.
Integrations
Ingestion integrations have global attributes as well as integration-specific attributes.
-
Global attributes apply to all ingestion integrations. They define event metadata stored as system attributes.
-
Integration-specific attributes are attributes available to one or more specified integrations.
When you enable multiple integrations on an IAM key, the IAM key stores any attributes set for all enabled integrations. See Multiple integrations on one key to learn how Lumi sequesters and assigns these attributes.
The following ingestion integrations only use global attributes and don't have any integration-specific attributes:
User attribute default values
Integration-specific attributes can define default values for mapping user attributes to Splunk® default fields.
For example, on an IAM key used for Splunk HEC, you can set a default value for the source user attribute. This attribute maps to the source field from Splunk.
Whether an integration includes attributes for these default fields, you can assign user attributes using your forwarding agent or a pipeline in Lumi.
Those values supersede any default values stored in IAM key attributes.
For example, the source metadata on an incoming event overrides the source value on the IAM key.
For details on how Lumi prioritizes assignment of user attributes, see Event model.
Global attributes
Global attributes apply to all ingestion integrations.
The global attributes are Environment and Team.
Lumi assigns these values to the env and team system attributes, respectively.
If you don't set the global attributes, Lumi doesn't set the system attributes.
The system attributes only apply within the scope of Lumi. See more information in system attributes.
Splunk HTTP attributes
Splunk HTTP attributes are known as HEC attributes in the Lumi UI. They apply to the integrations Splunk HEC and S2S over HTTP. They don't apply to S2S over TCP.
The following table describes the Splunk HTTP attributes:
| Attribute | Description | Example | User attribute if null |
|---|---|---|---|
| Source ( source) | Default value for the origin of the events sent to Lumi. The Lumi UI populates Source with http:IAM_KEY_NAME, which follows the default source name assignment in Splunk—http:TOKEN_NAME. Note that HEC token names are unique in Splunk, but IAM key names aren't unique in Lumi. | http:demo-key | N/A |
| Source type ( sourcetype) | Default value for the type of event data | access_combined | httpevent |
| Default index ( index) | Default value for the index attribute. The index is stored as a user attribute on the event, not as the event's repository. For details, see Lumi concepts for Splunk users. | main | main |
| Allowed indexes | Comma-separated list of allowed values for the index field | main, demo | N/A |
| Indexer acknowledgment | Option to enable the data protocol for HEC indexer acknowledgment. Lumi expects HEC requests to contain a channel ID and returns an acknowledgment ID in the response. Unlike Splunk, the acknowledgment in Lumi indicates receipt of the event and doesn't confirm event ingestion. | Checked | N/A |
Note that Allowed indexes and Indexer acknowledgment are indexing settings and don't correspond to any user attributes.
S2S attributes
S2S attributes apply to the S2S integrations for both tcpout and httpout.
Lumi doesn't store these attributes with the events.
These IAM key attributes configure event parsing for the S2S protocol. For more details, see Event parsing for S2S. To learn how S2S attributes relate to a Splunk configuration, see Lumi concepts for Splunk users.
The following table describes the S2S attributes:
| Attribute | Description | Example | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| Time prefix | String regular expression that matches the text pattern preceding the timestamp | [\w\.:]*\s[\w-]*\s[\w-]*\s\[ | Empty string |
| Max timestamp lookahead | Integer number that indicates the maximum character position to look for a timestamp. The position starts after the matched time prefix, if set. | 20 | 128 |
| Time format | String pattern in strptime format to extract timestamps | %d/%b/%Y:%H:%M:%S | Empty string |
| Should line merge | Boolean that controls merging of multi-line events | true | true |
S3 pull attributes
S3 pull attributes apply to the S3 pull integration that you use for recurring or backfill ingestion from objects in an S3 bucket.
To configure S3 pull, you must provide the ARN to authenticate Imply to your S3 bucket. Lumi doesn't store the ARN with the events.
You can optionally specify default values for the Splunk fields source, source type, and index. An attribute value set in a pipeline or sent with the event overrides the default value. If you don't assign a Splunk default field, Lumi doesn't store the user attribute.
In addition to the IAM key default values, Lumi assigns additional attributes specific to S3 pull ingestion. For more information, see Ingestion metadata.
The following table describes the S3 pull attributes:
| Attribute | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| AWS role ARN | Amazon Resource Name of your AWS IAM role. Imply assumes this role to access your bucket. | arn:aws:iam::012345678910:role/demo-role |
| Source ( source) | Default value to describe the origin of events | example-bucket |
| Source type ( sourcetype) | Default value to describe the event data | access_combined |
| Default index ( index) | Default value for the index | main |
Federated search attributes
Federated search attributes on a Lumi IAM key control how Splunk accesses and queries Lumi data.
The Data model attribute contains field mappings to translate between Lumi event fields and data model fields defined in Splunk. See Set up Splunk transparent federated search for details on how to configure the JSON object for this attribute.
Multiple integrations on one key
The following sets of attributes are shared across multiple ingestion integrations:
- Global attributes
- HEC attributes
- S2S attributes
Ensure that the values you define are compatible across its integrations. S3 pull attributes only apply to events sent using the S3 pull integration.
Note that the IAM key attributes for Splunk default fields are available for both HEC attributes and S3 pull attributes. Consequently, when you enable multiple integrations on the key, your IAM key could store two different sets of default values.
Consider the following example. You enable multiple integrations on an IAM key and set the index default value as follows:
| Integration | Has IAM key attribute for index | User-supplied value |
|---|---|---|
| Splunk HEC | Yes, in HEC attributes | auth |
| S2S over HTTP | Yes, in HEC attributes | auth (same as previous) |
| OTLP | No | N/A |
| S3 pull | Yes, in S3 pull attributes | main |
The following screenshot shows an example key with multiple integrations and different default index values:
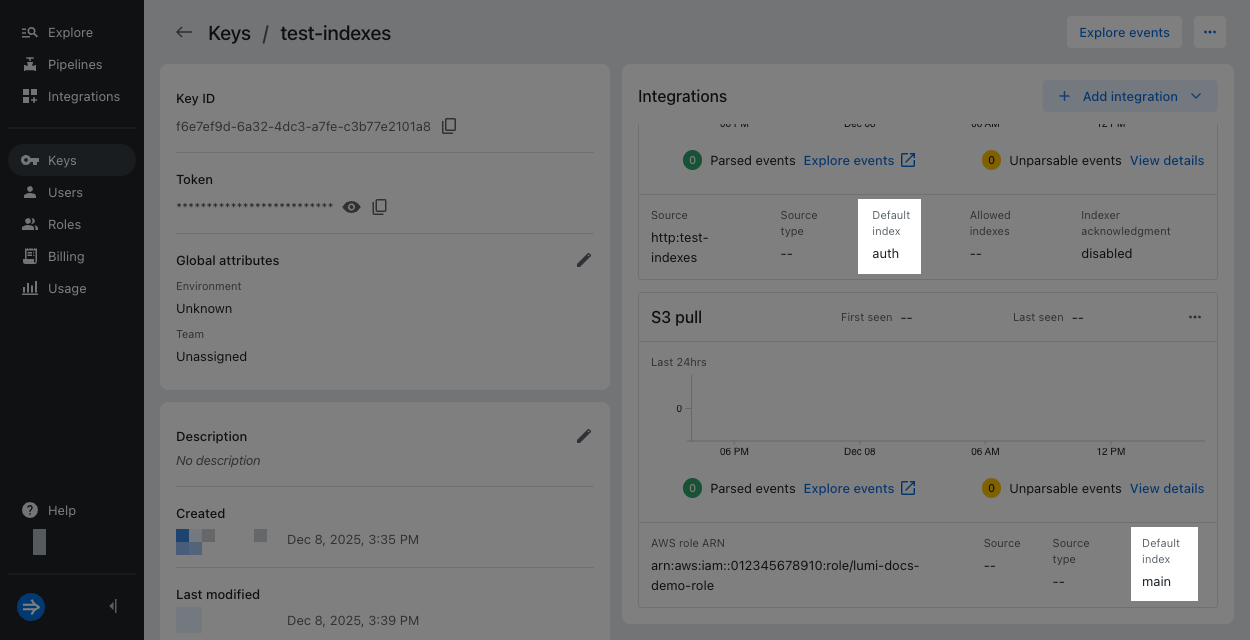
You don't send the index field as metadata with incoming events or create it in a pipeline so Lumi assigns the default IAM key value when available.
Lumi assigns index as follows:
- Events sent through Splunk HEC and S2S over HTTP store
index: auth. - Events sent through OTLP don't store
index. - Events sent through S3 pull store
index: main.
In other words, incoming events can store index differently depending on the integration used to send those events.
Since Splunk HEC and S2S over HTTP both share HEC attributes, if you change the default index for S2S over HTTP, it also changes the default index for Splunk HEC. It doesn't change the value for S3 pull.
For OTLP or any integration, you can assign index using a forwarding agent or pipeline.
See Index user attribute for more details on assignment of the index.
Learn more
For more information, see the following topics:
- Manage IAM keys to learn how to create an IAM key, add an integration, and set its attributes.
- Lumi concepts for Splunk users to learn about Splunk default fields in context of Lumi.
- Index user attribute more details on assigning the index user attribute.