IAM keys reference
IAM keys serve multiple purposes in Imply Lumi. You use IAM keys to send events to Lumi or configure federated search from Splunk®.
An IAM key designates permissions for sending or searching events. You can use the same IAM key for multiple applications. To authorize an IAM key for a specific use case, add the integration to the IAM key. When you add the integration, you can set any attributes specific to that integration.
This topic provides reference information on IAM keys. For details on creating and managing IAM keys, see Manage IAM keys.
Credentials
When you create an IAM key, Lumi provides the following details associated with the key:
- ID: A universally unique identifier (UUID) for the IAM key.
For example,7887140b-7707-4845-8aa3-a17095e00000. - Token: Credentials associated with the IAM key.
For example,229a2561-0000-0000-0000-bc433de16f89.
You use one or both values in your forwarding or search agent to authenticate requests to Lumi. For details on specific integration instructions, see the relevant topic in Send events and Search events.
IAM key attributes
An IAM key can store default values for select user attributes as well as parsing configuration for Splunk-to-Splunk (S2S). The attribute values and parsing settings are collectively described as IAM key attributes.
You can set IAM key attributes when you create the key. You can edit an existing key to update its attributes or add integrations and their respective attributes. Follow the steps to update an IAM key.
-
For ingestion integrations, global attributes apply to all integrations. Lumi stores the values as system attributes on the incoming events.
Select integrations support their own attributes, which you also configure on the IAM key. For example, they store event parsing settings or default values for user attributes. The attributes only apply when you use the IAM key with the associated integration.
-
For application integrations, no IAM key attributes apply. You only need the authentication details.
You can use the same key for multiple integrations. When you add a new integration to an existing key, be sure to determine whether the attributes set on the key are compatible across its integrations.
Global attributes
Global attributes apply to all ingestion integrations.
You can configure environment and team global attributes on any IAM key.
Lumi assigns these values to the env and team system attributes, respectively.
The system attributes only apply within the scope of Lumi.
HEC attributes
HEC attributes apply to the HEC integration and the S2S integration for httpout.
The attributes set default values for Splunk default fields and configure HEC forwarding. For details on how the HEC attributes relate to Splunk configuration, see Lumi concepts for Splunk users.
Whether you use HEC or another integration, you can also set user attributes using pipelines. For more information, see Transform events.
| Attribute | Description | Example | Lumi behavior when null |
|---|---|---|---|
| Source | Default value for the origin of the events sent to Lumi. The Lumi UI populates Source with http:IAM_KEY_NAME, which follows the default source name assignment in Splunk—http:TOKEN_NAME. Note that HEC token names are unique in Splunk, but IAM key names aren't unique in Lumi. | http:demo-key | Events don't store the attribute |
| Source type | Default value for the type of event data. | access_combined | Events store httpevent |
| Default index | Default value for the index attribute. The index is stored as a user attribute on the event, not as the event's repository. For details, see Lumi concepts for Splunk users. | main | Events store the system's default index |
| Allowed indexes | Comma-separated list of allowed values for the index field. | main, demo | N/A, not stored |
| Indexer acknowledgment | Select this option to use the data protocol for HEC indexer acknowledgment. Lumi expects HEC requests to contain a channel ID and returns an acknowledgment ID in the response. Unlike Splunk, the acknowledgment in Lumi indicates receipt of the event and doesn't confirm event ingestion. | Checked | N/A, not stored |
You may observe the same user attributes when you send events with S3 routing or S2S over TCP (tcpout).
The Splunk forwarding agent adds these attributes rather than Lumi.
S2S attributes
S2S attributes apply to the S2S integrations for both tcpout and httpout.
Events don't store the S2S attributes.
The attributes apply event parsing settings using a subset of Splunk props configuration. For more information, see Event parsing for S2S. For details on how the S2S attributes relate to Splunk configuration, see Lumi concepts for Splunk users.
Regardless of integration, you can also parse events using pipelines. For more information, see Transform events.
| Attribute | Description | Example | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| Time prefix | String regular expression that matches the text pattern preceding the timestamp. | [\w\.:]*\s[\w-]*\s[\w-]*\s\[ | Empty string |
| Max timestamp lookahead | Integer number that indicates the maximum character position to look for a timestamp. The position starts after the matched time prefix, if set. | 20 | 128 |
| Time format | String pattern in strptime format to extract timestamps. | %d/%b/%Y:%H:%M:%S | Empty string |
S3 pull attributes
The S3 pull attribute applies to the S3 pull integration. Events don't store the S3 pull attribute.
The attribute authenticates access to your S3 bucket using your Lumi IAM key. |---|---|---|---|
Attribute precedence
Metadata sent with the raw event, such as assigned by a forwarding agent, override IAM key attributes.
For example, an event that has the source metadata doesn't use the source value on the IAM key.
For details on how Lumi prioritizes assignment of user attributes, see Event model.
IAM key metrics
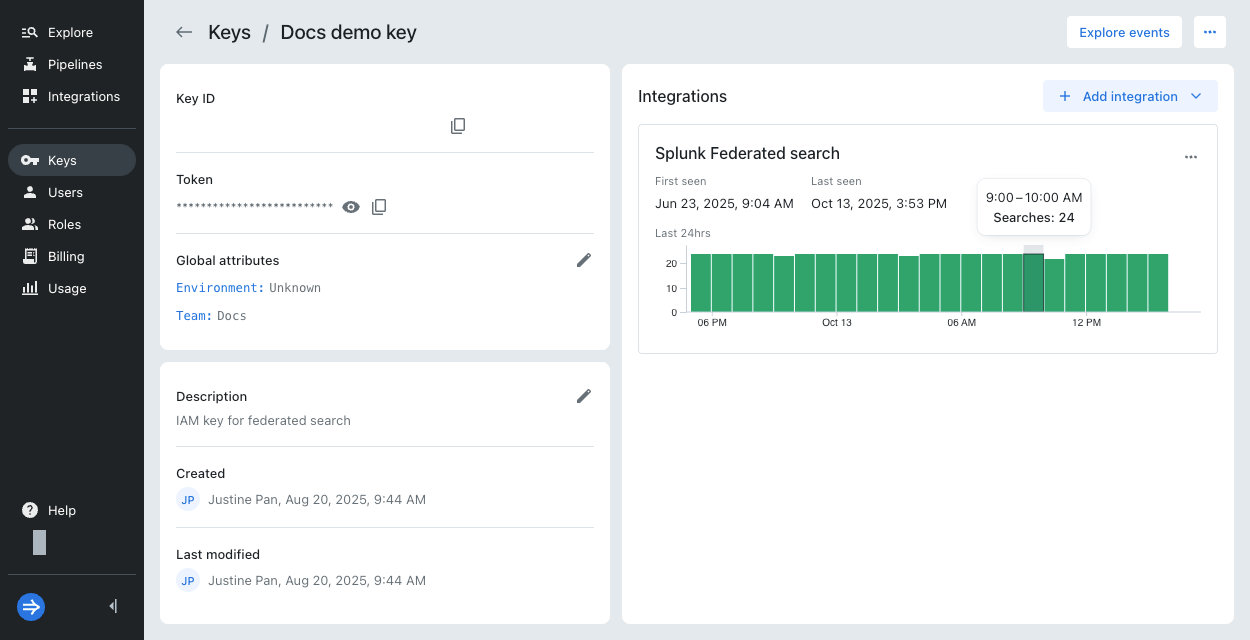
Select an IAM key to view metrics related to the key. Hover over a bar to see the key usage during that hour.
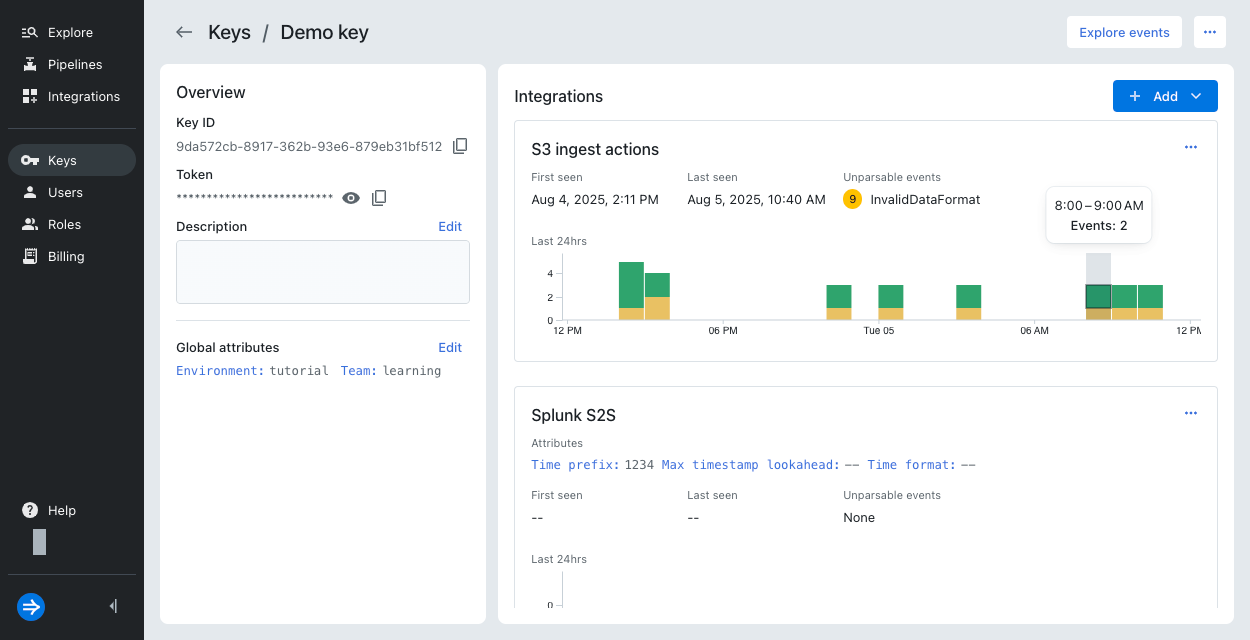
For ingestion integrations, the color of the bar indicates the event status:
- Green: Successful events
- Yellow: Unparsable events
For application integrations, a green bar indicates the number of searches run in that hour.
For details on troubleshooting unparsable events, see Troubleshoot data ingestion.
Learn more
For more information, see the following topics:
- Manage IAM keys for details on creating and managing IAM keys.
- Monitor usage for details on usage dashboards and metrics.
- Monitor billing to view usage in the context of billing.