Query Lumi events with data models
AI summary
About AI summaries.
Data models in Splunk® provide a structured way to organize and search data using standardized field names. This topic provides an overview of how Imply Lumi integrates with Splunk data models and outlines the requirements for configuring data model queries.
For setup instructions, see Set up transparent federated search.
Workflow
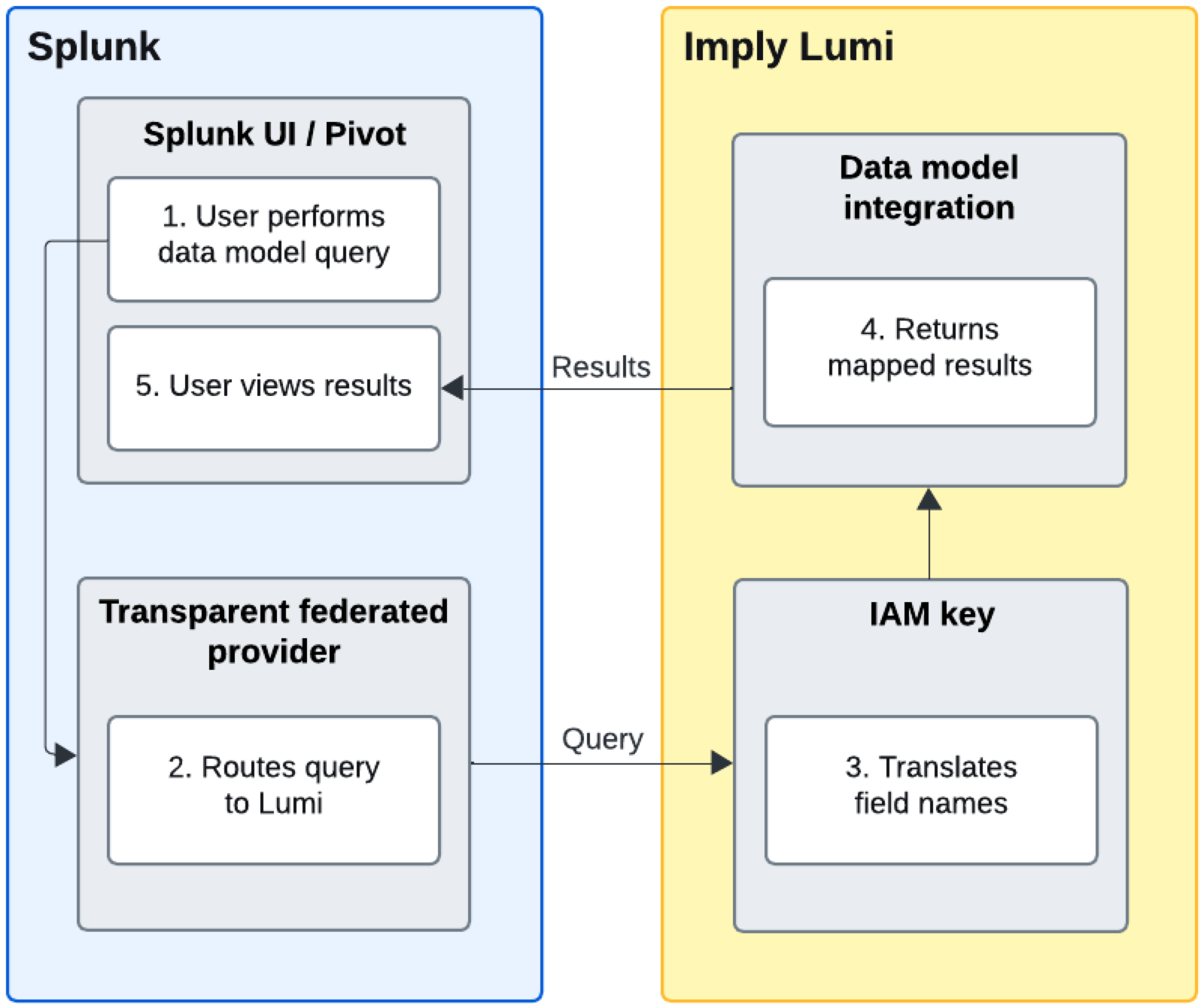
The following workflow describes how Splunk data models query data in Lumi:
- A user performs a local query in Splunk or runs a Pivot report using a data model (for example, the Common Information Model (CIM) Web data model).
- A transparent federated provider routes the query to Lumi.
- Lumi translates the data model field names to its own field names using field mappings on the IAM key.
- Lumi returns results to Splunk with field names translated back to match the data model.
- In Splunk, the user sees results combined from both Splunk and Lumi.
The following example illustrates this process in more detail.
Example workflow
In an example scenario, a user wants to investigate a spike in 500 errors on GET requests to a specific web server. They want to filter results from the past hour to identify whether there's a current service issue.
1. User creates a report in Splunk Pivot UI
The user selects the Web data model and builds a Pivot report with the following filters:
dest=web-prod-01status=500http_method=GET- Time range: Last hour
The data model must be accelerated for Pivot queries to work. See Data model acceleration for details.
Behind the scenes, Splunk creates a query like:
| tstats count FROM datamodel=Web.Web WHERE Web.dest="web-prod-01" Web.status=500 Web.http_method=GET earliest=-1h by Web.http_method
2. Transparent federated provider passes query to Lumi
The transparent federated provider routes the query to Lumi with the data model field names: Web.dest, Web.status, Web.http_method.
3. Lumi translates field names
Lumi receives the query and uses the IAM key mapping to translate the incoming field names:
Web.dest→hostWeb.status→statusWeb.http_method→method
Note that status uses the same field name in both Lumi and the data model, but must still be included in the field mapping to appear in query results.
See Field mapping for details.
Lumi executes the query using its native field names: host, status, method.
After retrieving matching events, Lumi translates the field names back to what the data model expects:
host→Web.deststatus→Web.statusmethod→Web.http_method
4. Lumi returns mapped results
Lumi returns events with field names matching the Web data model specification: Web.dest, Web.status, Web.http_method.
5. Splunk displays results
The Pivot report displays results from both Lumi and local Splunk indexes, with all events using consistent Web data model field names.
Requirements
The following requirements apply when you query Lumi with Splunk data models.
Splunk requirements
Configure the following in Splunk to enable data model queries to Lumi.
Data model acceleration
To query Lumi through Splunk Pivot, accelerate the data model in Splunk. For manually defined searches that reference a data model, acceleration is not required. See Accelerate data models in the Splunk documentation for more information.
If you attempt to use Pivot with a non-accelerated data model, Splunk transforms the query to use inline filters and calculations. Lumi doesn't recognize this as a data model query and returns empty results.
Lumi requirements
Configure the following in Lumi to ensure data model queries return complete results.
Field mapping preparation
Field mapping requires that your Lumi events already have extracted fields that correspond to the data model fields. The IAM key configuration provides field name translation only—it doesn't perform field extraction, evaluation, or calculation.
When you query Lumi through a transparent federated provider, Splunk's search-time eval expressions and field extractions don't execute.
If your Lumi data contains raw events (for example, raw Apache logs), or if your data model relies on calculated fields or complex extractions, you must use Lumi pipelines to extract and transform fields before configuring the data model integration.
Field mapping
Include all fields that the Splunk data model expects in the IAM key field mapping, including fields where the Lumi field name matches the data model field name. Lumi returns empty columns for unmapped fields.
The special data model fields _time, source, sourcetype, and host are an exception—all Splunk data models inherit them so Lumi automatically maps them.
You don't need to add them to your field mappings.
A single IAM key can support multiple data models.
You can map fields from multiple data models to the same Lumi field.
For example, you can map both the Web data model's dest field and the Network Traffic data model's dest field to Lumi's host field.
No search-time field evaluation
When you query Lumi through a transparent federated provider, Splunk's search-time eval expressions and field extractions don't execute.
Field mapping requires that your Lumi events already have extracted fields that correspond to the data model fields—the IAM key configuration provides field name translation only, not field extraction, evaluation, or calculation.
You must define all field transformations at index time using Lumi pipelines to ensure the fields are available for queries. In particular, you might need to transform data in Lumi when:
- Your Lumi data contains raw events (for example, raw Apache logs).
- Your data model relies on calculated fields or complex extractions.
Multiple federated provider modes
Imply doesn't recommend running both standard and transparent mode federated providers simultaneously against the same Lumi instance.
Learn more
See the following topics for more information:
- Set up Splunk standard federated search to set up a standard federated provider in Splunk.
- Set up Splunk transparent federated search to set up a transparent federated provider in Splunk.
- IAM key attributes for details on IAM key attributes.