How to transform events with pipelines
AI summary
About AI summaries.
In this tutorial, you learn how to transform events coming into Imply Lumi using a pipeline. A pipeline is an ordered list of processors that operate on events that meet specific search criteria. A processor performs a distinct task based on its type and processing rules.
The steps show you how to:
- Create a pipeline and add processors to the pipeline.
- Configure processors to extract attribute values, map attributes, and remove attributes.
- Send events to Lumi with and without using a pipeline.
- Compare user attributes with and without pipeline processing.
The following diagram summarizes the end-to-end process of processing events in Lumi. Click any box in the diagram to jump to that step.
Prerequisites
To complete the tutorial, you need the following:
- Access to Lumi with the Data manager role or higher.
For information on roles and permissions, see Manage roles. - An application that can send HTTP requests, such as a Unix terminal or Postman.
This tutorial shows example requests using the command-line tool curl.
1. Send an event
In this section, you send an event to the HTTP event collector.
-
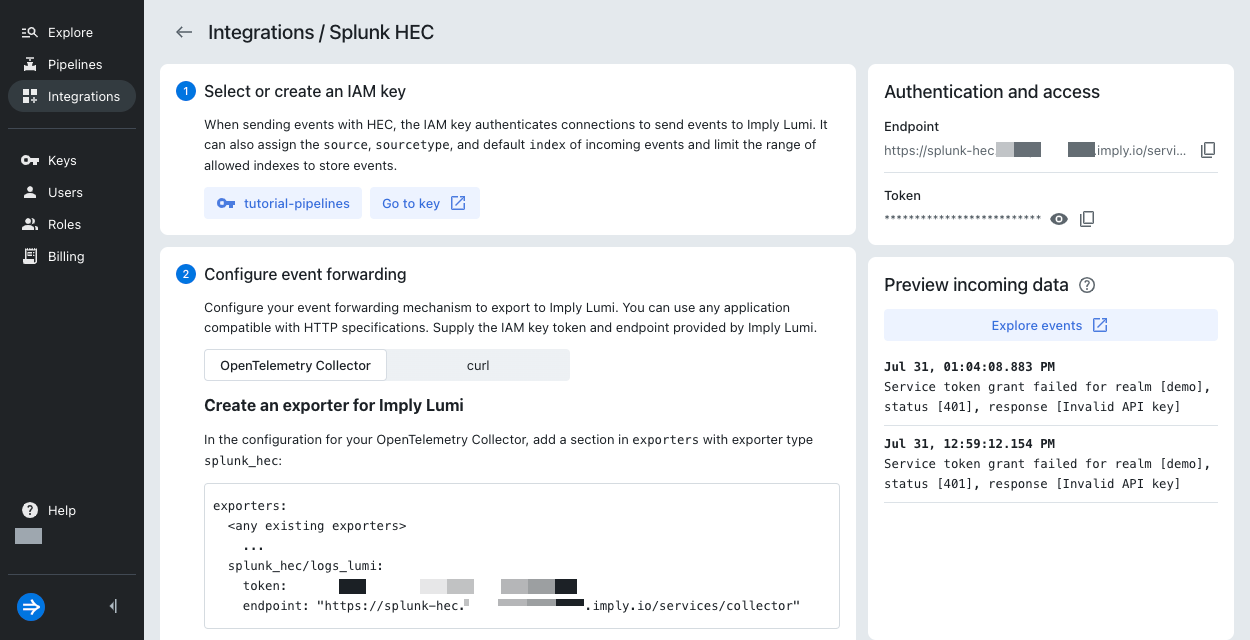
In the Lumi navigation menu, click Integrations > Splunk® HEC.
-
In the Select or create an IAM key pane, click Select or create key > Create key.
-
For the IAM key, enter the name
tutorial-pipelines. Leave all other fields empty. -
Click Create.
-
In the Configure event forwarding pane, select the
curltab.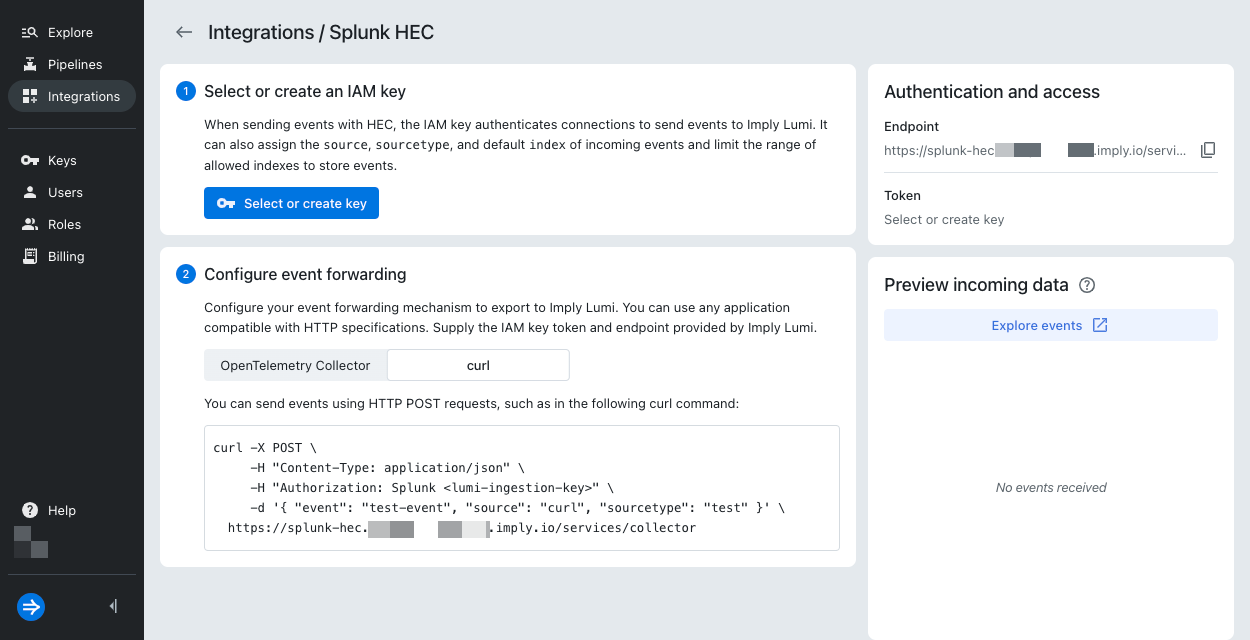
-
Copy and paste the command into a text editor.
-
Replace the example JSON data with the following object:
{"event": "Service token grant failed for realm [demo], status [401], response [Invalid API key]", "source": "curl", "fields": {"userid": "wilma", "status": 401}}Your command should look similar to the following:
curl -X POST \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Splunk IAM_KEY_TOKEN" \
-d '{ "event": "Service token grant failed for realm [demo], status [401], response [Invalid API key]", "source": "curl", "fields": {"userid": "wilma", "status": 401}}' \
LUMI_ENDPOINT -
Copy and paste the command into a terminal and submit the request.
-
In the Preview incoming data pane, confirm that you see the new event.
2. Create a pipeline
In this section, you create a pipeline that will process all events that meet the specified condition.
-
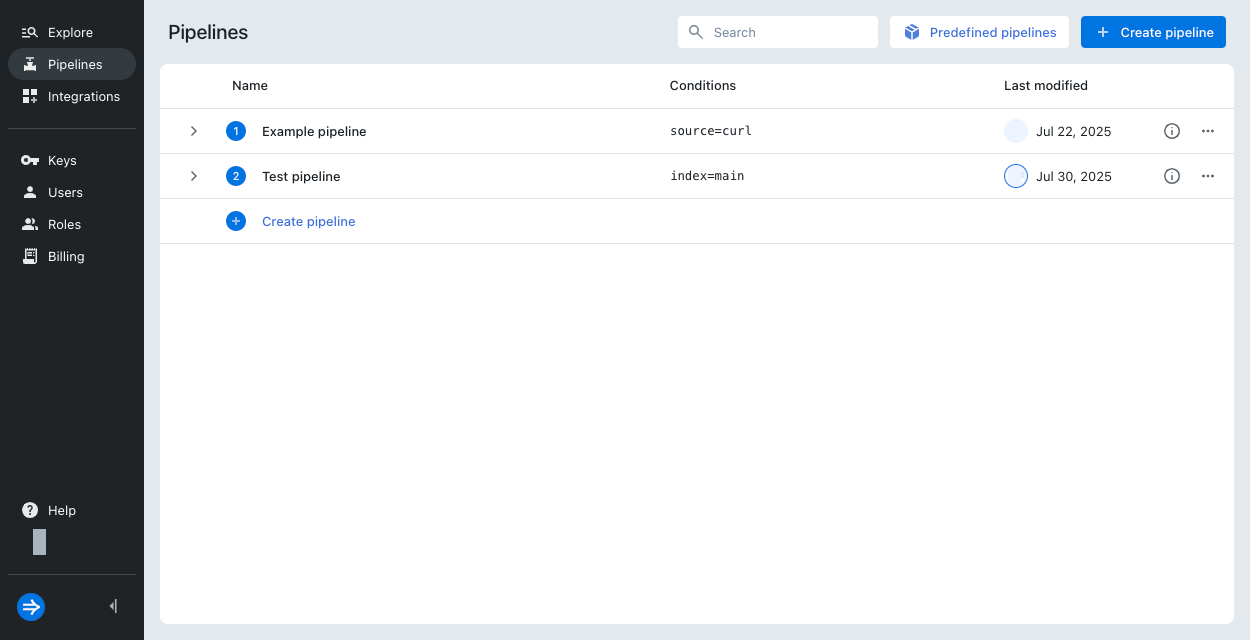
In the Lumi navigation menu, click Pipelines.
-
Click + Create pipeline.
-
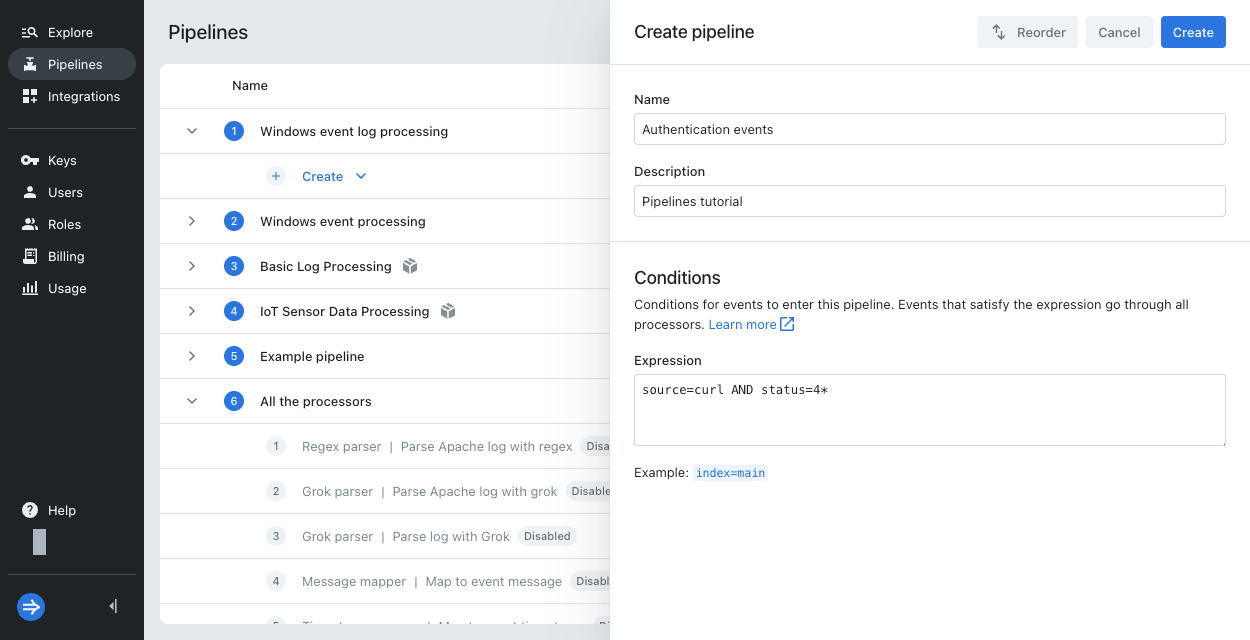
Enter pipeline details:
- Name:
Authentication events - Description:
Pipelines tutorial - Expression:
source=curl AND status=4*
- Name:
-
Click Create.
3. Add processors
In this section, you add processors, which are components of a pipeline that perform individual processing tasks.
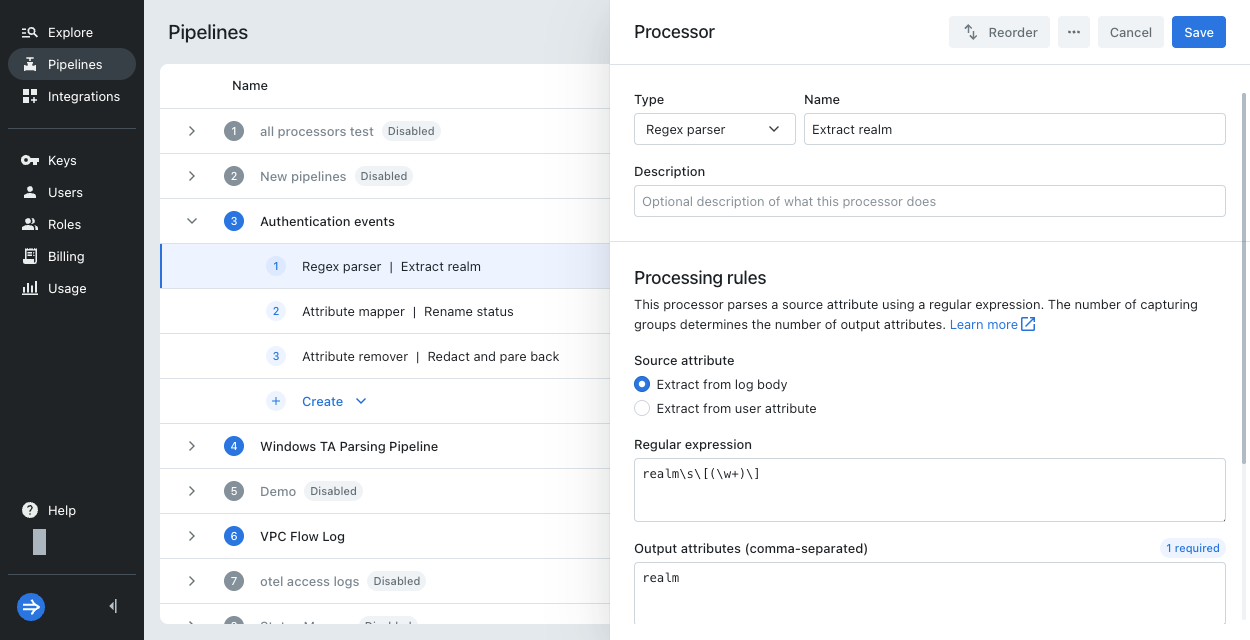
Regex parser
First, add a regex parser to extract the name of the realm from the event message.
-
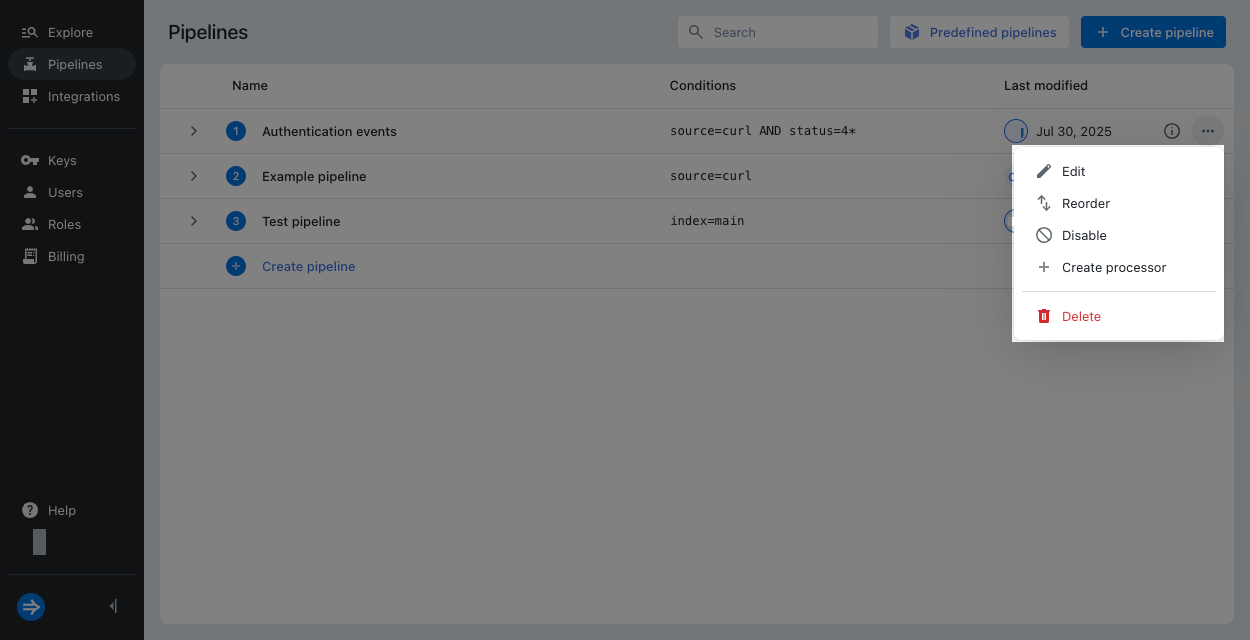
On the Pipelines page, click the ellipsis next to the pipeline.
-
Click Create processor.
-
Enter processor details:
- Type:
Regex parser - Name:
Extract realm - Source attribute: Select
Extract from log body - Regular expression:
realm\s\[(\w+)\]
This regular expression looks for the formatrealm [NAME], whereNAMEis the extracted element. - Output attributes:
realm
The processor stores the value in a user attribute namedrealm.
- Type:
-
Scroll down to try out the regular expression. In Sample, enter the following event:
Service token grant failed for realm [demo], status [401], response [Invalid API key] -
The Expected output now shows the result
demo. This value populates therealmuser attribute when the event message is as listed.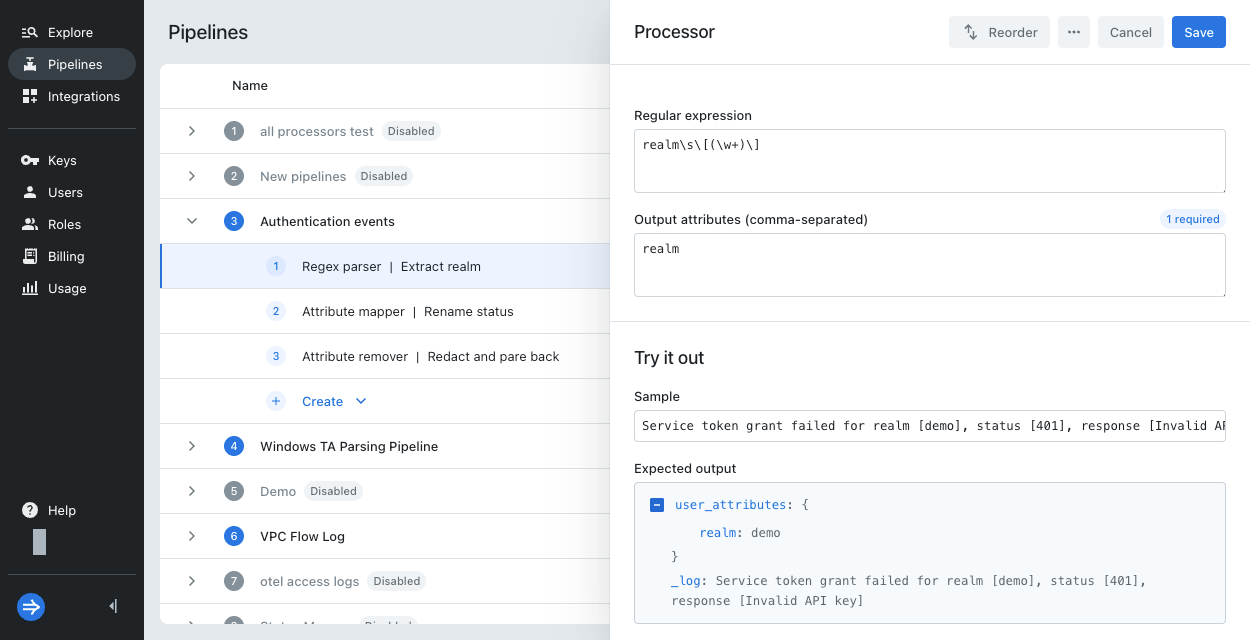
Attribute mapper
Next, add an attribute mapper to rename status to http_status.
-
On the Pipelines page, click the ellipsis next to the pipeline.
-
Select Create processor.
-
Enter processor details:
- Type:
Attribute mapper - Name:
Rename status - Source attribute:
status - Output attribute:
http_status
- Type:
-
Leave the override toggle unselected.
-
Optionally, try out the processor. In Sample user attributes, enter the following:
{"source": "curl", "userid": "wilma", "status": 401, "realm": "demo"}The expected output shows both
statusandhttp_status. You removestatusin the next step.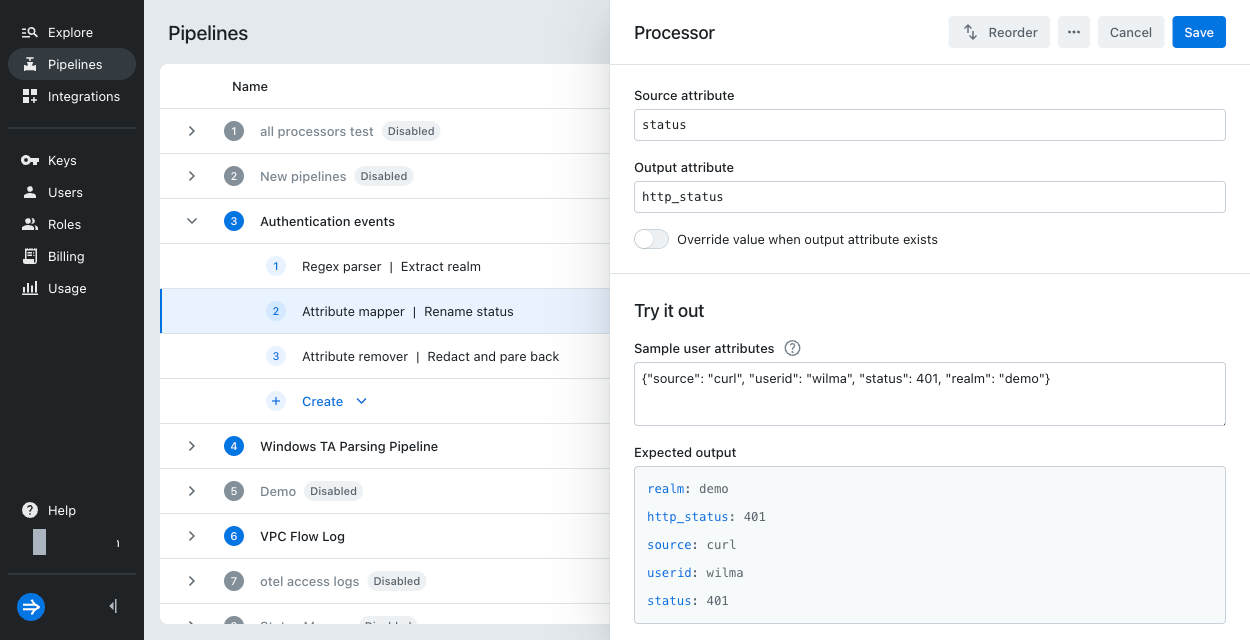
-
Click Create.
When you try out the processor, you enter a JSON that contains the input user attributes. Notice that this is similar to the JSON event you sent with curl, with the following differences:
- Removes
eventsince the event message isn't relevant to this processor. - Includes
realmthat was generated in the previous step. - Promotes
useridandstatusas top-level JSON elements. The sample doesn't havefieldssince it's only used to send user attributes with Splunk HEC.
Attribute remover
Finally, add an attribute remover to remove userid and status.
In this scenario, you remove userid to redact personal information associated with the event,
and you remove status since you now store its information in http_status.
-
On the Pipelines page, click the ellipsis next to the pipeline.
-
Select Create processor.
-
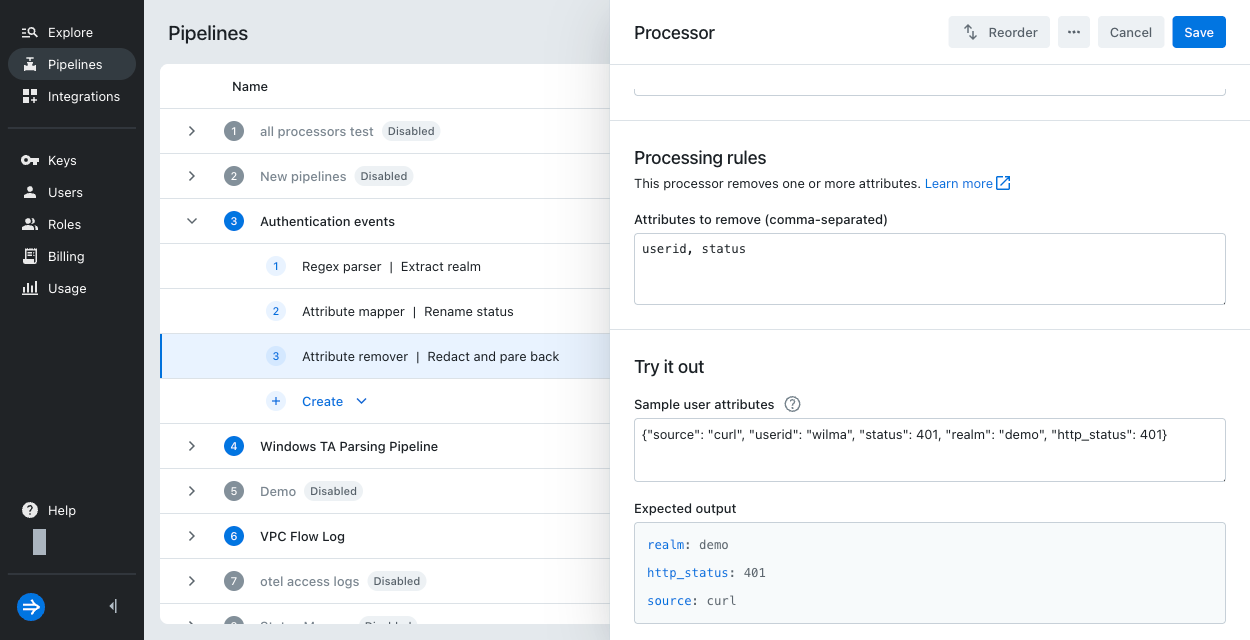
Enter processor details:
- Type:
Attribute remover - Name:
Redact and pare back - Attributes to remove:
userid, status
- Type:
-
Optionally, try out the processor. In Sample user attributes, enter the following:
{"source": "curl", "userid": "wilma", "status": 401, "realm": "demo", "http_status": 401}The expected output shows the final set of user attributes.
-
Click Create.
4. Observe the difference
In this section, you send another event to the HTTP event collector and compare the results.
- Follow the steps in Send an event to send a new event using the
tutorial-pipelinesIAM key. - In the Preview incoming data pane, confirm that you see the new event.
- Click Explore events.
- Adjust the time filter if needed to display both events.
- Notice the difference between the events.
The processed event includes user attributes forrealmandhttp_status.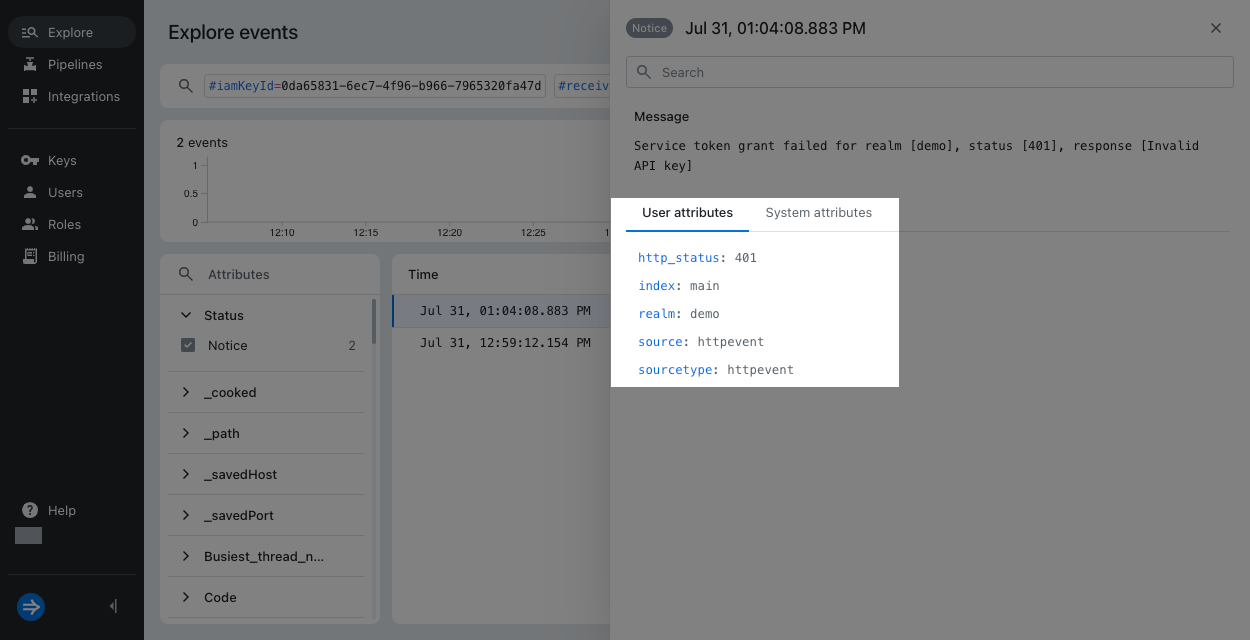 The unprocessed event doesn't have
The unprocessed event doesn't have realmbut includesuseridandstatus.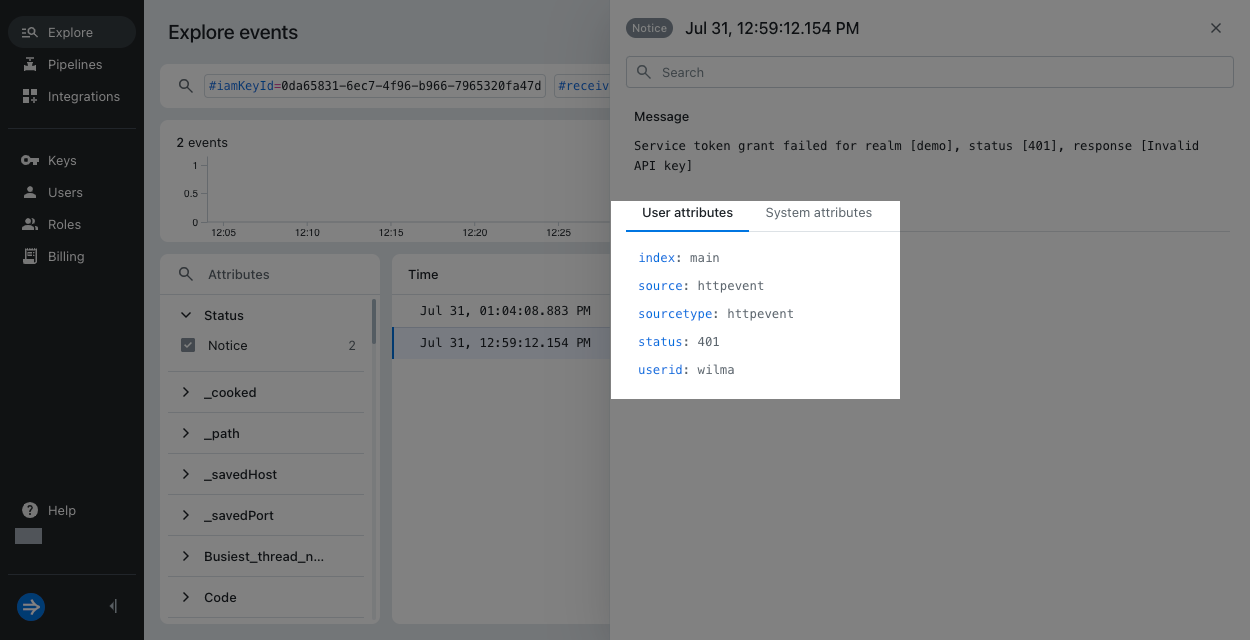
Explore further
To explore more with pipelines, try the following activities:
- Send an event that already includes the
http_statusattribute. In the attribute mapper, view how the result changes when you toggle the override setting on or off. - Disable a processor in the pipeline and compare the results.
- Create a second pipeline with the same conditions and note the order of operations.
Learn more
See the following topics for more information:
- Transform events using pipelines for an overview of pipelines and processors.
- Manage pipelines and processors for how to create and manage pipelines and processors.
- Processors reference for the types of processors available in Lumi.