How to search events with Splunk
AI summary
About AI summaries.
This tutorial builds on the Quickstart and walks you through how to:
- Configure federated search to connect Splunk® to Imply Lumi.
- Perform federated queries on Lumi events.
The steps assume that, as part of the Quickstart, you've already:
- Added web logs to Lumi using the file upload feature.
- Viewed and queried events in Lumi.
To complete the steps, you use sample web traffic data from a fictional online store. For background on the dataset and its format, see the tutorial data overview.
The following diagram summarizes the end-to-end process of searching events with Splunk. Yellow shaded boxes represent steps taken within Lumi, and blue shaded boxes represent steps taken outside Lumi. Click any box in the diagram to jump to that step.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, download an up-to-date version of the sample log file and upload it to Lumi.
To complete the tutorial, you need the following:
- Access to Lumi with the Viewer role or higher.
For information on roles and permissions, see Manage roles. - A Lumi IAM key with the federated search integration.
See Create an IAM key for details. - A Splunk user with the
admin_all_objectsandindexes_editcapabilities. The following roles have these capabilities by default. See the Splunk documentation on security for federated search for more information.- Splunk Cloud:
sc_admin - Splunk Enterprise:
admin
- Splunk Cloud:
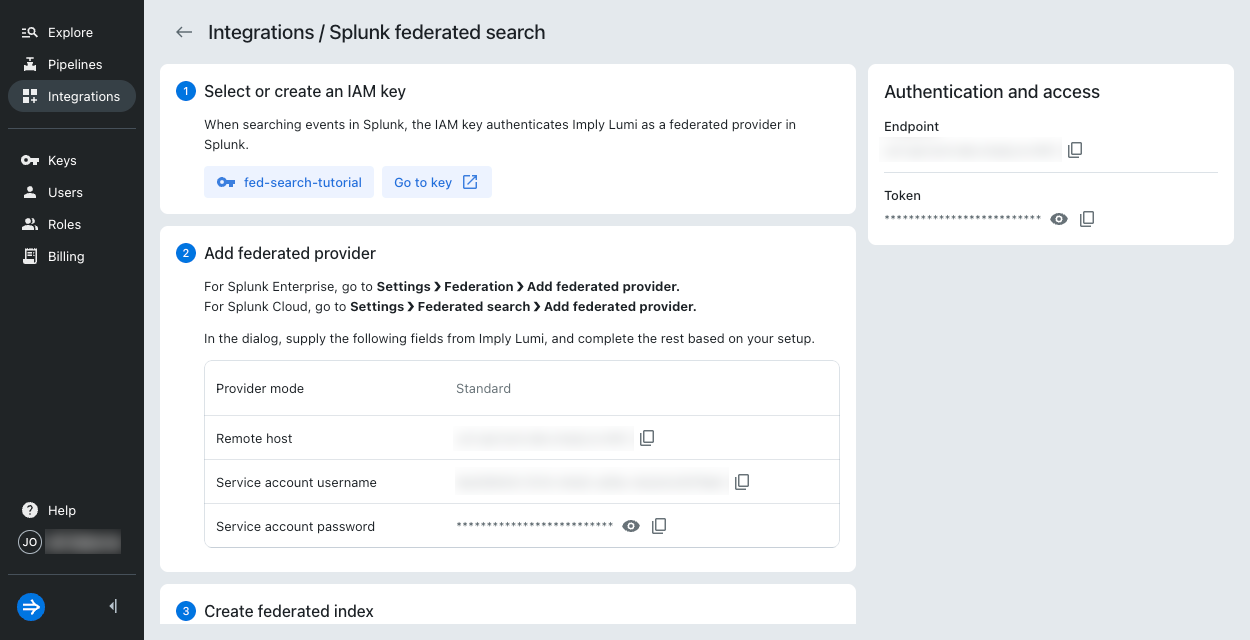
1. Retrieve details from Lumi
In this step, you retrieve the information you need from Lumi.
- In Lumi, go to Integrations > Federated search.
- Click Select or create key.
- Select your IAM key in the drop-down menu and click Select.
- If prompted, click Add to enable the key for the integration.
- Copy the Remote host, Service account username, and Service account password. You'll need these details in the next steps.
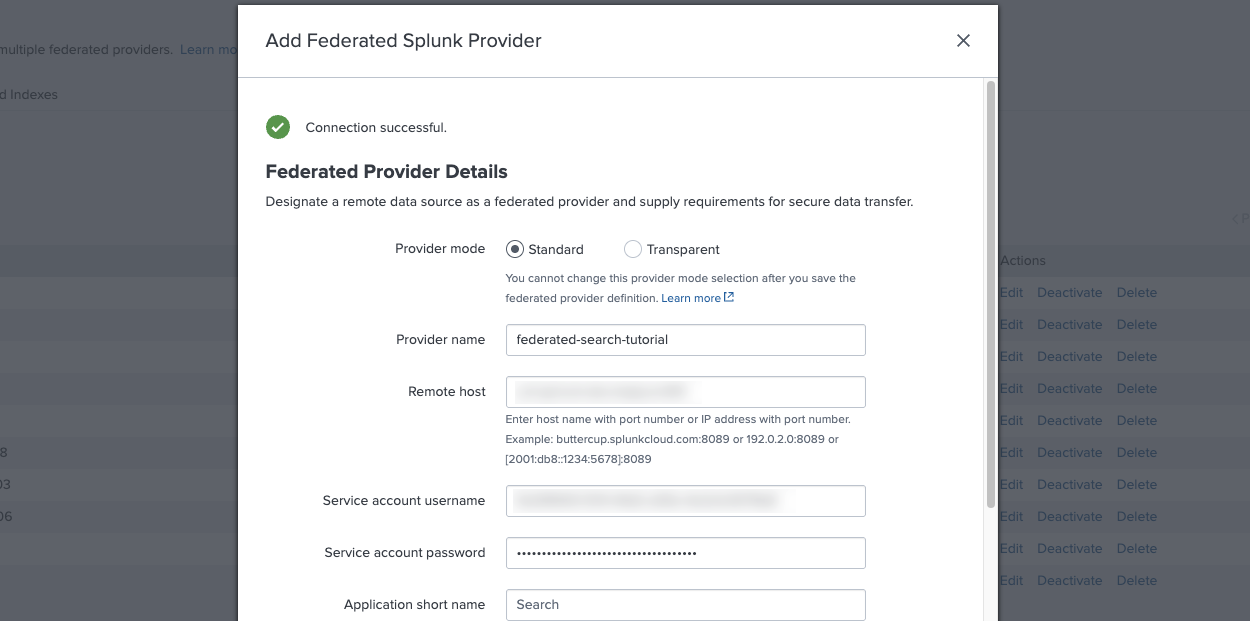
2. Create a federated provider
In this step, you add Lumi as a federated provider in Splunk. The federated provider connects to Lumi using your IAM key and Lumi host details.
- In Splunk Web, go to Settings ❯ Federation ❯ Add federated provider.
- Enter the following fields to integrate with Lumi:
- Provider mode:
Standard. - Provider name:
federated-search-tutorial. - Remote host: Remote host you copied in the previous step.
- Service account username: Service account username you copied in the previous step.
- Service account password: Service account password you copied in the previous step.
- Provider mode:
- Leave all other fields unchanged and click the Agree checkbox.
- Test the connection.
- Once the connection is successful, click Save.
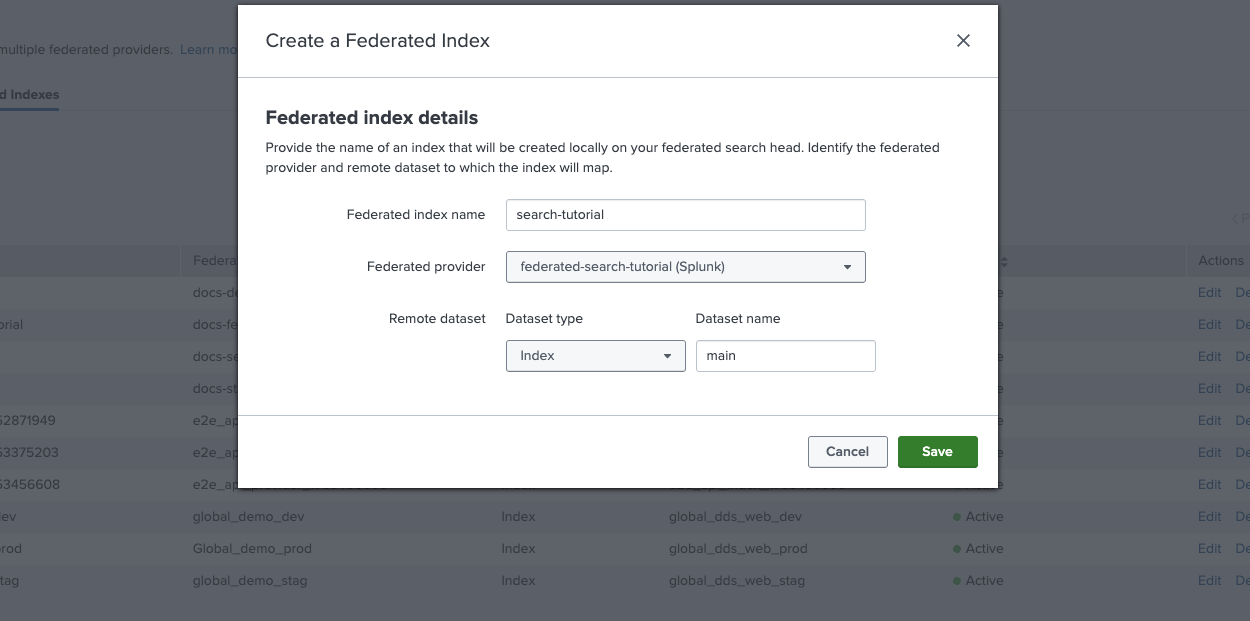
3. Create a federated index
In this step, you create a federated index in Splunk.
The federated index connects to an index in Lumi.
In this case, the index is set to main in the sample data.
- In Splunk Web, go to Settings ❯ Federation ❯ Add federated index.
- Select For Splunk to Splunk provider.
- Complete the following fields:
- Federated index name:
search-tutorial - Federated provider:
federated-search-tutorial - Remote dataset type:
Index - Dataset name:
main
- Federated index name:
- Click Save.
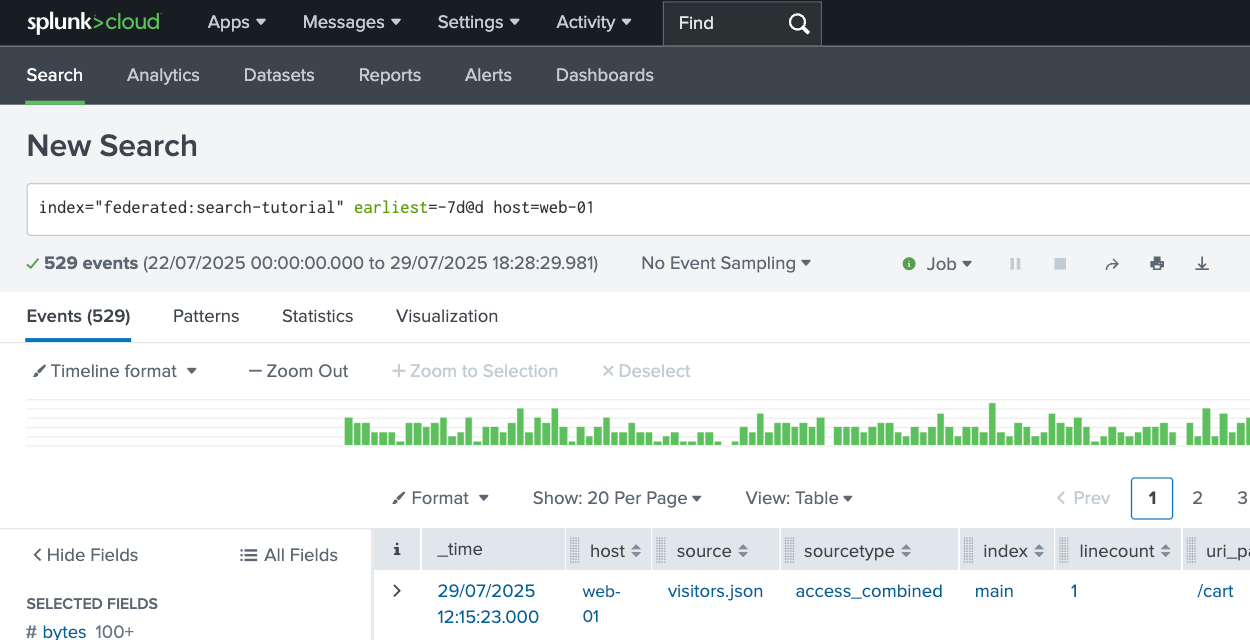
4. Test federated search
In this step, you test your federated search setup.
- In Splunk Web, go to the Search & Reporting app.
- Set the time range to the last 7 days.
You can also include
earliest=-7d@dtimes in the query as shown below, which overrides the time range selector. - Enter the following query:
index="federated:search-tutorial" earliest=-7d@d host=web-01
This returns events from the sample log file in Lumi and includes host to filter out any other events in the same time range.
5. Run federated queries
In this step, you run a series of federated queries to explore site traffic, identify errors, understand request patterns, and enrich the data with a calculated field.
-
List the top 5
uriby access count:index="federated:search-tutorial" earliest=-7d@d host=web-01
| top uri limit=5Example output:
uricountpercent/categories19136.105860/admin7714.555766/cart7213.610586/468.695652/search315.860113 -
Show events with
status500 or higher, and count how many times eachstatusoccurred:index="federated:search-tutorial" earliest=-7d@d host=web-01
| where status >= 500
| stats count by statusExample output:
statuscount5001150213503165046 -
Find all requests for a particular user with
statusnot equal to 200, and display the specified fields in a table:index="federated:search-tutorial" earliest=-7d@d host=web-01
| where status != 200
| where user = "gusosborne"
| table _time user status uri_pathExample output:
_timeuserstatusuri_path2025-07-29 02:58:09gusosborne403/categories/smart-lighting/app-controlled-lamp2025-07-25 15:26:02gusosborne401/categories/led-lighting/ultra-bright-led-bulb2025-07-25 16:53:47gusosborne304/product/eclipse-wall-sconce2025-07-29 02:51:29gusosborne403/2025-07-25 16:53:47gusosborne304/cart -
Show average
bytesper method, rounded to 2 decimal places:index="federated:search-tutorial" earliest=-7d@d host=web-01
| stats avg(bytes) as avg_bytes by method
| eval avg_bytes = round(avg_bytes, 2)Example output:
methodavg_bytesDELETE4752.27GET4726.69OPTIONS1235.00POST5241.57PUT5092.28 -
Extract the operating system from the
useragentfield, count how often each OS appears, and display the five most common ones:index="federated:search-tutorial" earliest=-7d@d host=web-01
| rex field=useragent "\((?<os>[^;]+);"
| stats count by os
| sort -count
| head 5Example output:
oscountMacintosh189Windows NT 10.0139Linux114iPhone28Windows NT 6.120 -
Add a field to mark responses with
bytesgreater than 5000:index="federated:search-tutorial" earliest=-7d@d host=web-01
| eval big_response = if(bytes > 5000, "yes", "no") | table bytes, big_responseExample output:
bytesbig_response4701no1178no8070yes2237no9497yes
Learn more
To build on this tutorial, follow How to convert a Splunk dashboard for federated search to update a Splunk dashboard to use federated search queries against Lumi.
See the following topics for more information:
- Federated search reference for federated search examples using SPL commands, functions, and expressions that Lumi supports.
- Search events with Splunk for details on configuring federated search of Lumi events within Splunk.
- Splunk command reference for more information on SPL commands and examples of SPL queries.