Manage pipelines and processors
AI summary
About AI summaries.
In many cases you might want to transform the events you send to Lumi before storing them. For example, you want to extract key details from a raw event message into new attributes for your observability analyses. In Lumi, you process incoming events using pipelines. A pipeline contains one or more processors that define the data processing tasks. For a conceptual overview of pipelines, see Transform events with pipelines.
This topic walks you through the process to create and manage pipelines and processors. You'll learn how to:
- Create a pipeline and define conditions for events to enter the pipeline
- Add processors to perform operations such as parsing text or assigning user attributes
- Update pipelines and processors to reorder, disable, or delete them
- View the pipelines that processed an event
In addition to your own custom processing rules, Lumi offers several predefined pipelines. A predefined pipeline has a preset list of processors tailored to a specific event type, such as Windows event logs. Predefined pipelines are enabled by default. For more information, see Work with predefined pipelines.
To follow along with a tutorial, see How to transform events with pipelines.
Prerequisites
To create and manage pipelines in Lumi, you need the Data manager role or higher. For information on roles and permissions, see Manage roles.
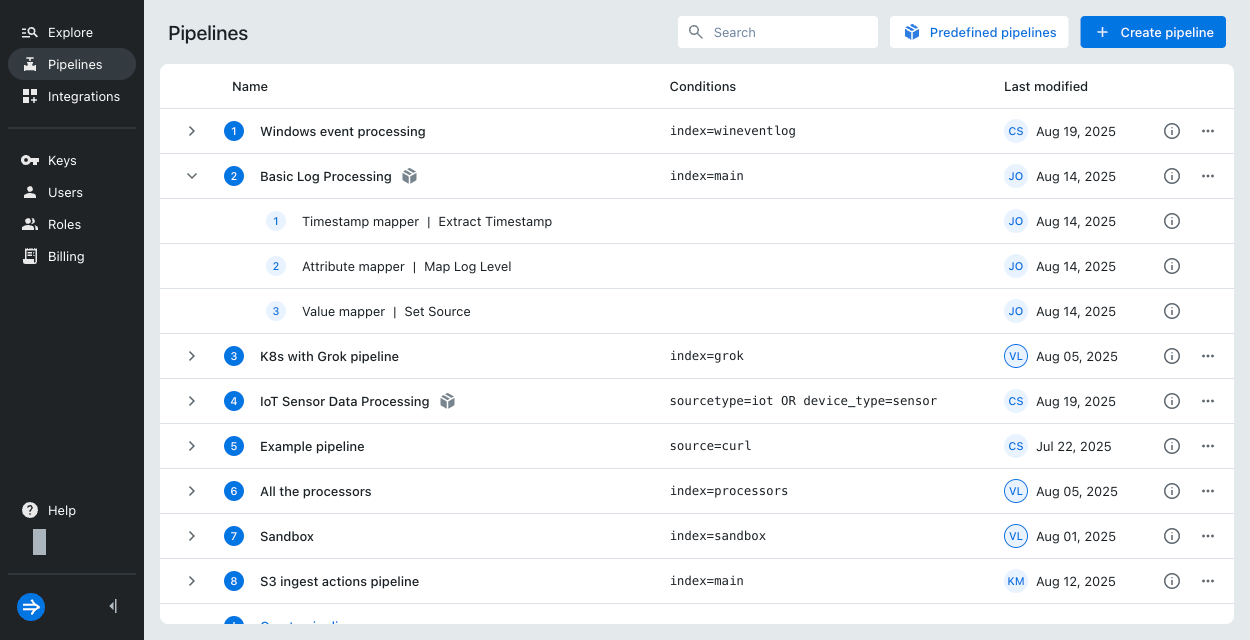
View pipelines
The Pipelines page shows a list of all pipelines. Expand any pipeline to see the processors in the pipeline. Click the information icon next to a pipeline or processor to view its description and the date it was last modified.
Create a pipeline
You can create a pipeline with your own processors or use a predefined pipeline provided by Lumi. To use a predefined pipeline, see Work with predefined pipelines.
If you already have an existing pipeline and want to create a nested pipeline within it, see Work with nested pipelines.
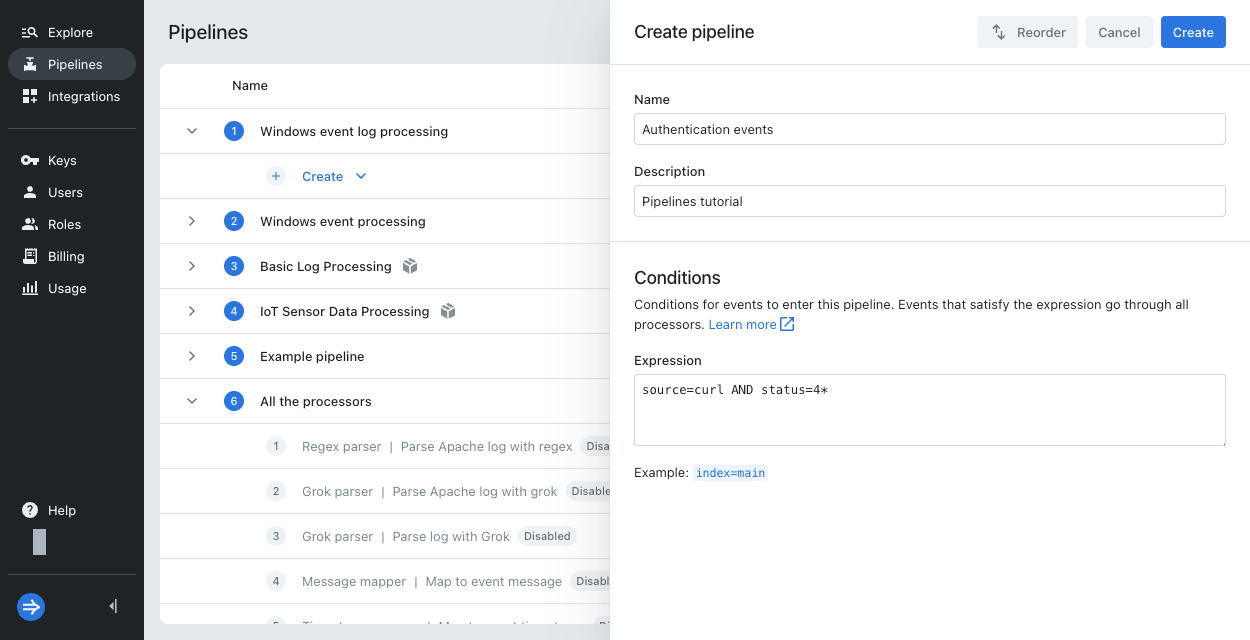
To create your own pipeline:
- Click Pipelines from the navigation menu.
- Click + Create pipeline.
- Enter pipeline details:
- Name: Name to identify the pipeline.
- Description: Optional description for the pipeline.
- Expression: Query that qualifies events for the pipeline. For more details and examples, see Pipeline conditions.
- Click Create.
- Optionally, update the pipeline to reorder its position.
Create a processor
Add functionality to a pipeline by creating one or more processors.
To create a processor in a pipeline:
- Click Pipelines from the navigation menu.
- Select a pipeline, then click Create > Processor.
- Select the processor type.
- Enter a name and optional description for the processor.
- Fill in the processing rules. The available fields depend on the processor type.
- For guidance on how to specify attributes, see Processor settings.
- For a reference on all available processors, see Processors.
- Optionally, try out the processor.
- Click Create.
- Optionally, update the processor to reorder its position.
Try out a processor
To preview how a processor operates, use the Try it out section to enter sample data and view the processed output.
Sample input
The format of the sample input depends on the processor:
- Some processors have the input field Sample user attributes, in which you provide a JSON object containing source attribute names and their values.
- Other processors use the input field Sample, where you enter only the string value, such as the event message.
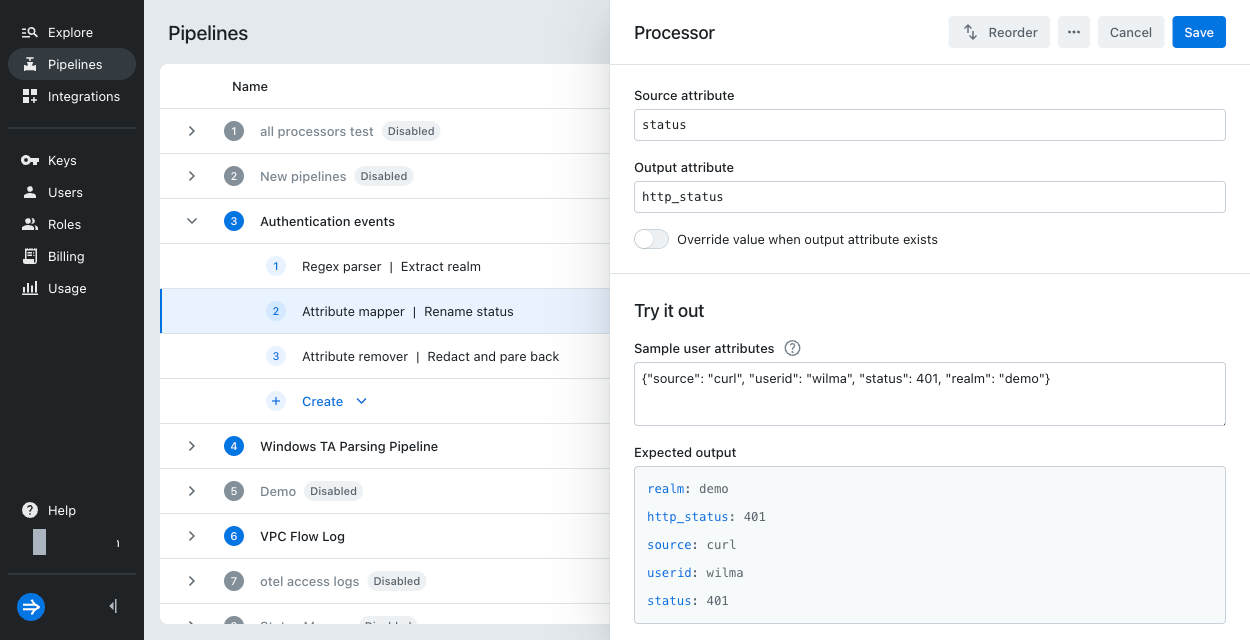
Sample user attributes: Attribute mapper
The attribute mapper is an example of a processor that samples using source attribute name and values.
Example input:
{"source": "curl", "userid": "wilma", "status": 401, "realm": "demo"}
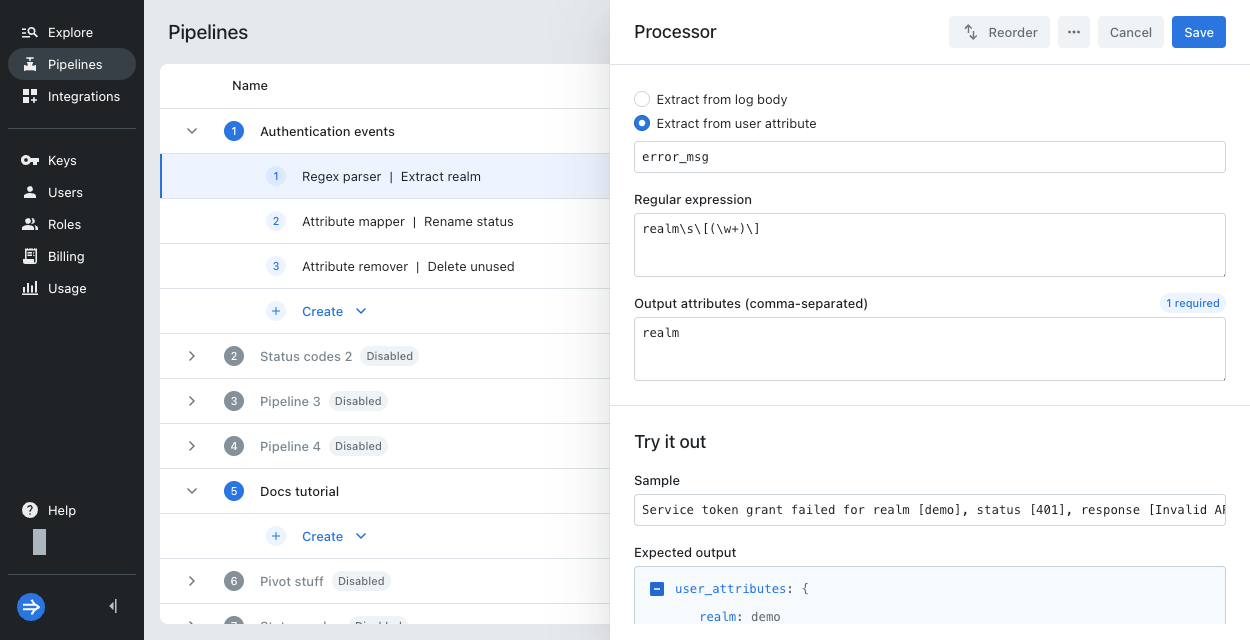
Sample value: Regex parser
The regex parser is an example of a processor that samples directly from the attribute value. Even though you might select Extract from user attribute as the source, you don't supply the user attribute name in the sample.
Example input:
Service token grant failed for realm [demo], status [401], response [Invalid API key]
Sample value: Key-value parser
The key-value parser also takes only a sample value without the attribute name.
For example, if you have an attribute called cloud which stored the JSON {"platform": "aws_eks", "provider": "aws", "region": "us-east-1"},
you only enter the JSON object in the sample without including the attribute name cloud.
Enter a sample that corresponds to the pattern you selected in the processor configuration.
Example inputs for each parser pattern:
- Equality:
key=value - JSON:
{"key1": "val1", "key2": {"key3": "val3"}} - Regex:
key:val1 key:val2 key:val3for the regex(\w*):(\w*) - XML:
<root><key>value</key></root>
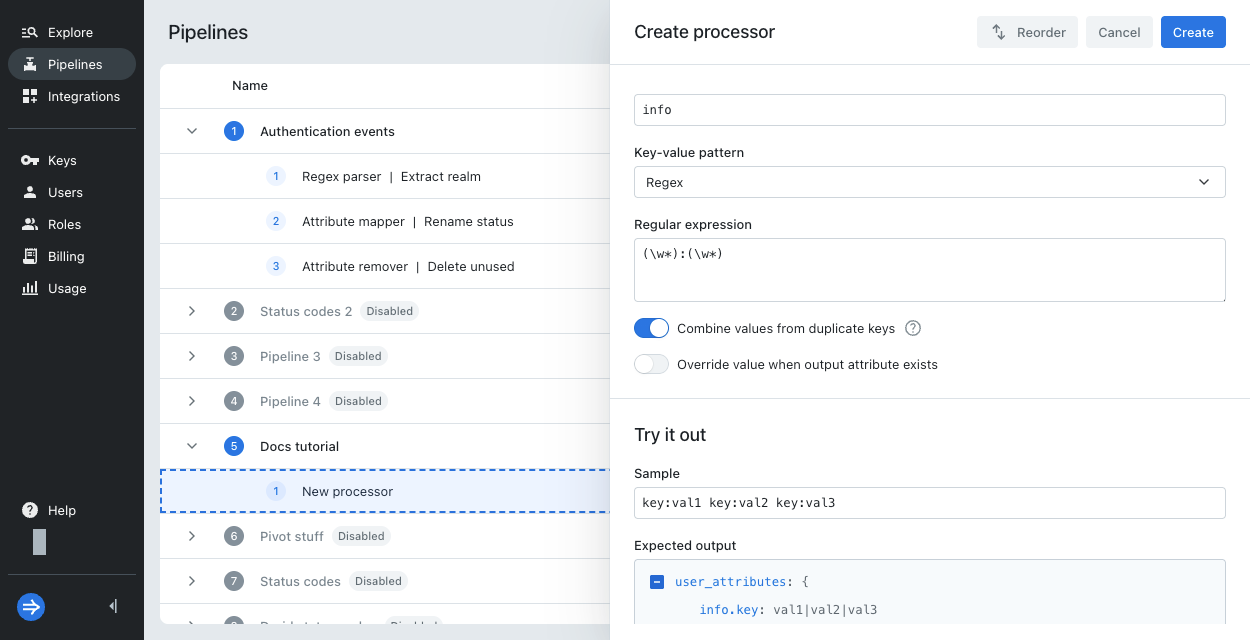
Sample output
View the processed results in Expected output. The output might show the user attributes directly, for example:
source: my_app
sourcetype: access_combined
The output can include the event message. In this case, the user attributes are within user_attributes, and the event message is in _log. For example:
user_attributes: {
status: ok
}
_log: Deployment successful. System 1 status: [ok] System 2 status: [alert]
Note that the expected output doesn't include the event timestamp.
Simulate pipelines
You can simulate your existing pipelines to preview the entire flow of processing for one or all pipelines.
Note the following details when providing sample events to simulate:
- You can sample a maximum of 100 events.
- Format the samples in one of the supported Event formats. You can't mix format types.
- To test a specific pipeline, ensure your events satisfy the pipeline conditions.
For example, if the condition is
host=192*, a sample event containing the metadata"host": "192.0.2.1"would go through processing. You can also set default attribute values, described in the following steps, to match a pipeline condition.
To simulate pipelines:
-
Click Pipelines from the navigation menu.
-
To simulate all pipelines, click Simulate in the top right.
To simulate a single pipeline, click the ellipsis next to the pipeline and select Simulate. -
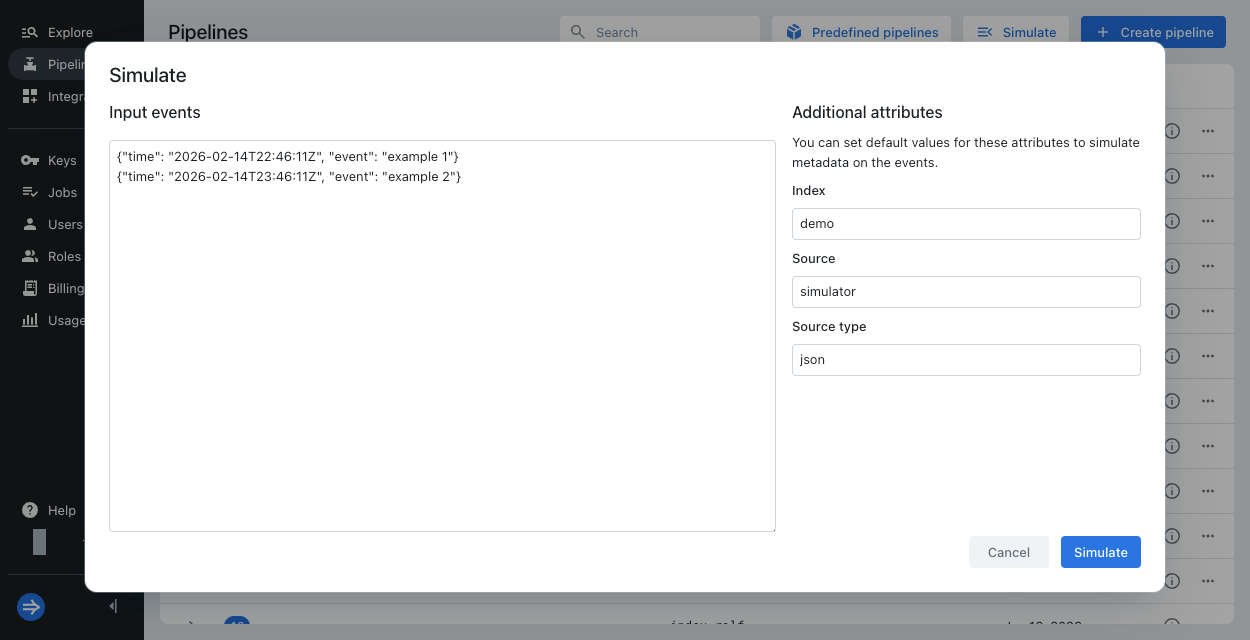
In the dialog, enter your sample events in Input events.
Plain text example:
test event 1
test event 2Splunk® HEC JSON example:
{"time": "2026-02-14T22:46:11Z", "event": "example 1"}
{"time": "2026-02-14T23:46:11Z", "event": "example 2"}Generic JSON example:
{"time": "2026-02-14T22:46:11Z", "log": "example 1", "host": "192.0.2.1"}
{"time": "2026-02-14T23:46:11Z", "log": "example 2", "host": "203.0.113.0"} -
Optionally enter default values for Index, Source, and Source type. The user attributes
index,source, orsourcetypestore the respective values. You can use these fields to satisfy a pipeline condition, view how a processor uses or transforms the attribute, or simply view the created attribute on the processed event.Lumi only assigns these values when they're not already specified in the event or assigned by a pipeline. This follows the same behavior as default values on an IAM key.
-
Click Simulate.
-
Lumi shows the processed events. Click an event to see its details.
The following screenshot shows simulated results for the Splunk HEC JSON sample events. In this example, the pipeline uses the condition
index=demoand contains value mappers to assignidanduser.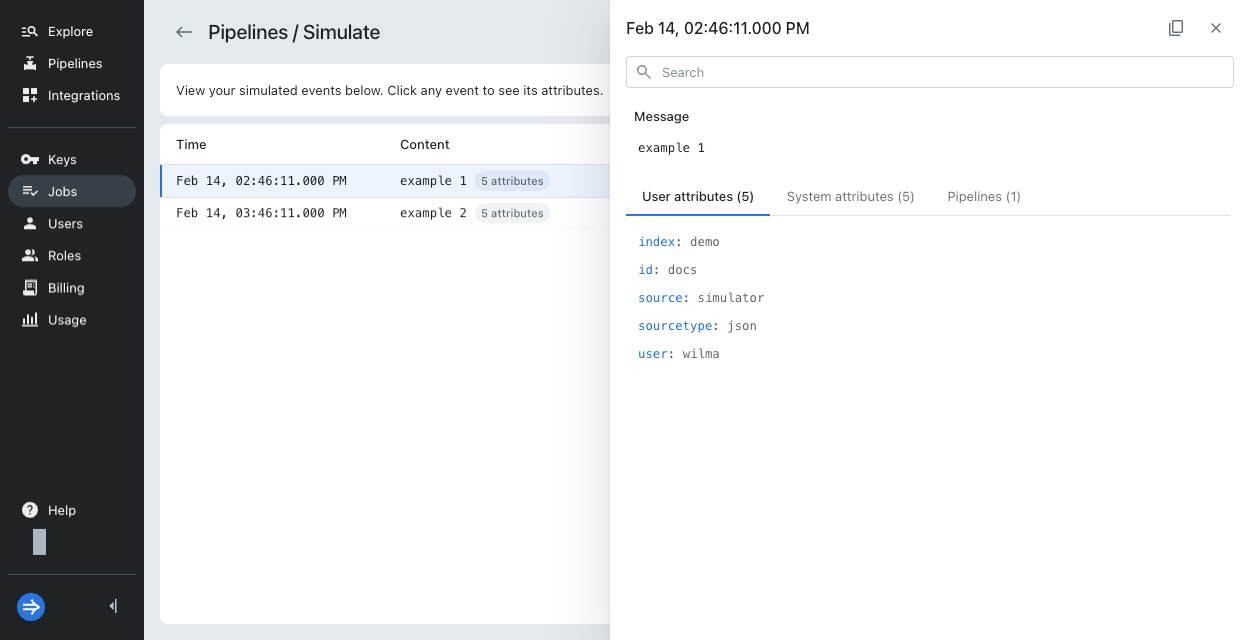
-
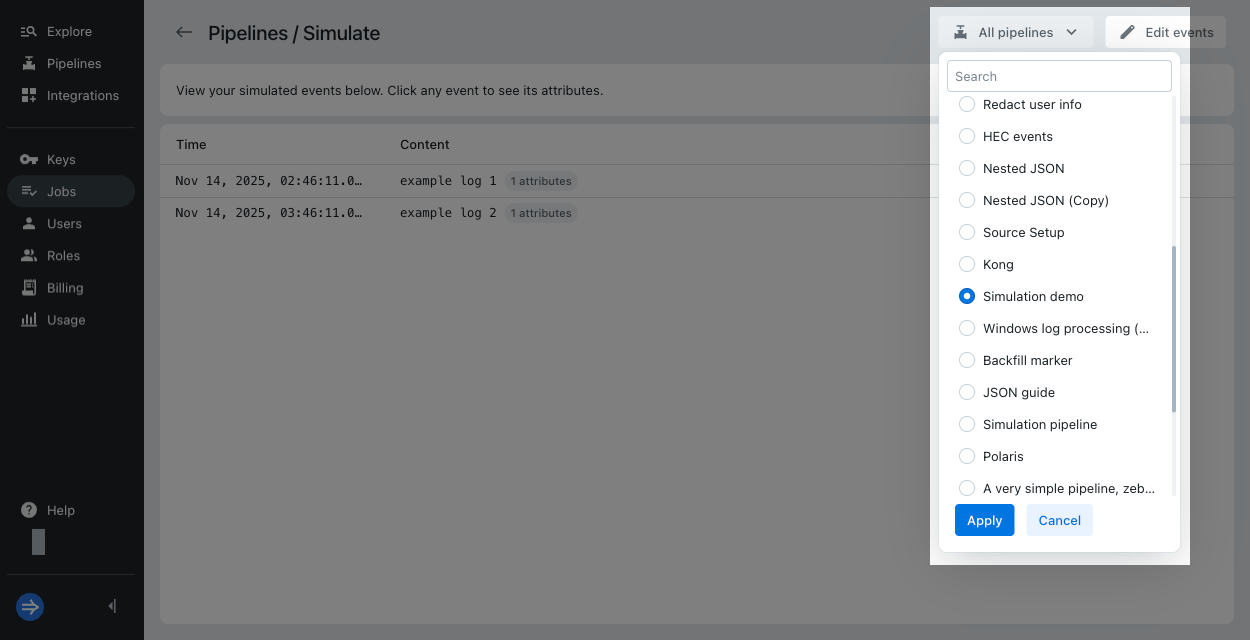
To change which pipeline to simulate, click the drop-down in the top right corner and select your pipeline.
-
Optionally select Edit events to update the sample events or default attribute values.
Update a pipeline or processor
To update a pipeline or processor:
- Click Pipelines from the navigation menu.
- For the processor you want to update, click the ellipsis and select Edit.
- Make the desired changes then click Save.
From the ellipsis menu, you can also take the following actions:
- Reorder
- Duplicate
- Simulate
- Enable or disable
- Delete
- Create processor (for pipelines)
When you create a new pipeline or processor, Lumi enables it by default. Disabled elements appear dimmed in the pipelines list.
View pipelines for a processed event
To view the pipelines that processed an event:
- Go to the explore view and find the event.
- Select the event to open its event details pane.
- If the event was processed, Lumi displays a tab called Pipelines. The list displays pipelines in order of processing.
- Click a pipeline to view it in the Pipelines page. Lumi expands the specific pipeline you selected.
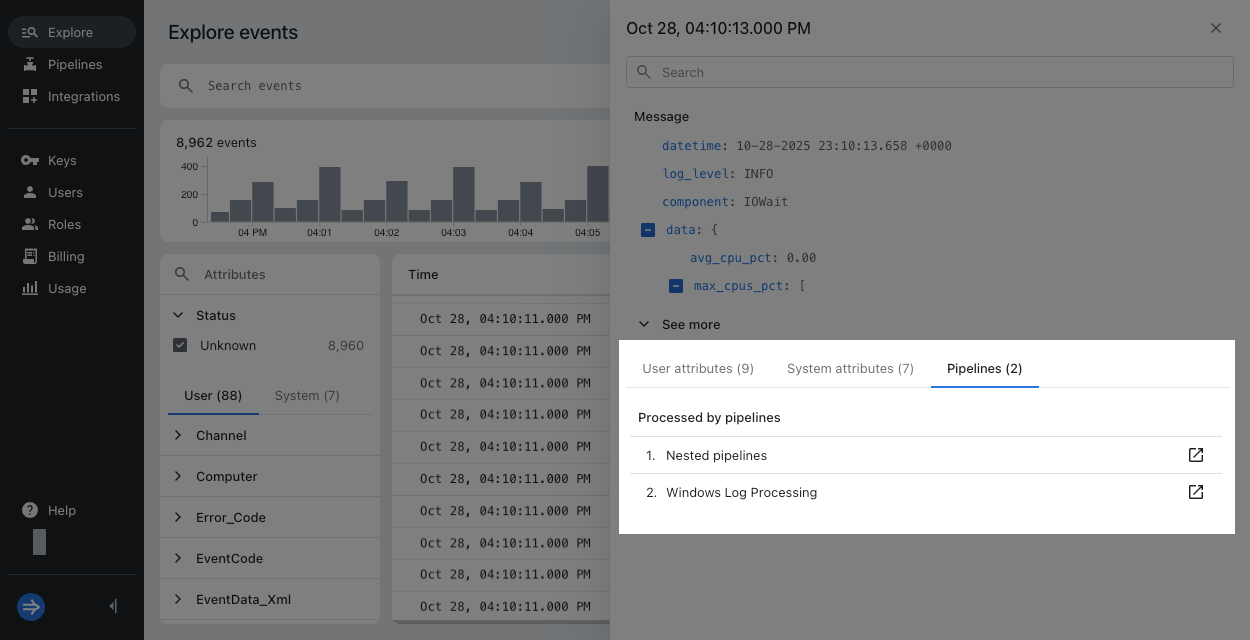
After you delete a pipeline, Lumi retains the pipeline ID. If an event was processed by a deleted pipeline, the list shows the pipeline ID and its deleted status. You can't view the conditions and processors for a deleted pipeline.
Learn more
See the following topics for more information:
- Transform events using pipelines for an overview of pipelines and processors.
- How to transform events with pipelines for a tutorial on using pipelines.
- Processors reference for the types of processors available in Lumi.
- Predefined pipelines for curated pipelines for specific data sources.
- Nested pipelines for organizing pipelines using nesting.