Visualizations
Imply provides a wide array of expressive visualizations that enable fast, interactive exploration of your data. Visualizations are not static charts. You can interact directly with them by clicking on various graphical elements to select data segments for drill-down and deeper analysis.
When you change the shown dimensions, Pivot chooses the best visualization for the selected dimensions automatically.
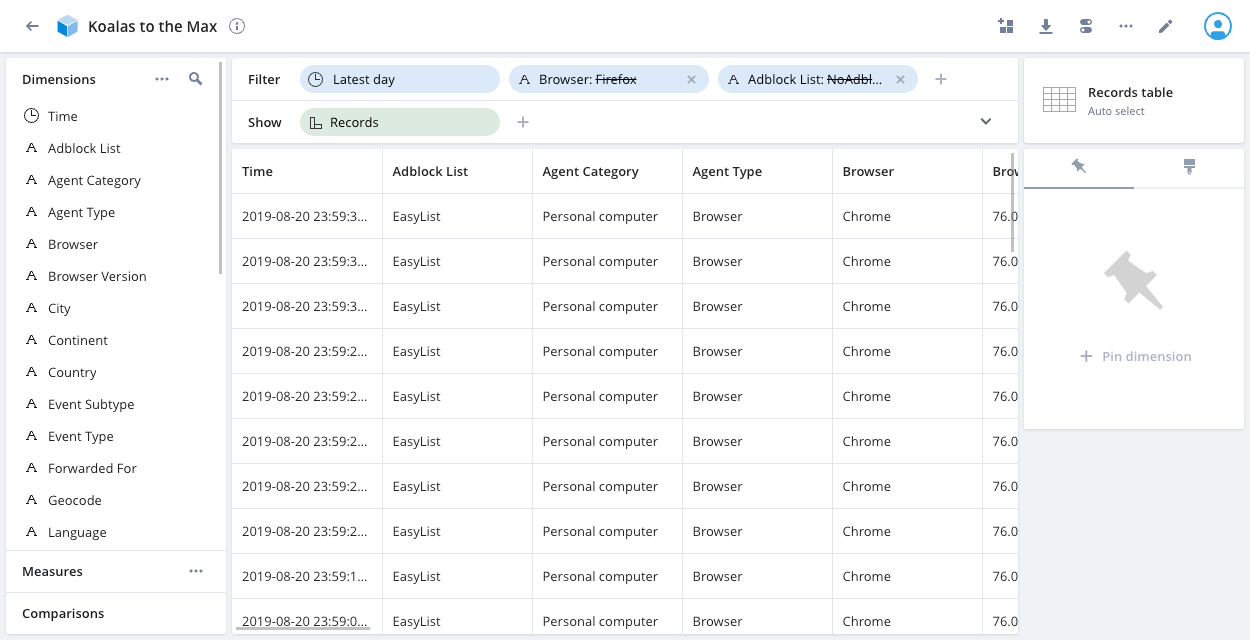
To select an alternative visualization, click the current visualization type on the right side of the screen to display the visualization selector. The following example shows Records table as the current visualization:
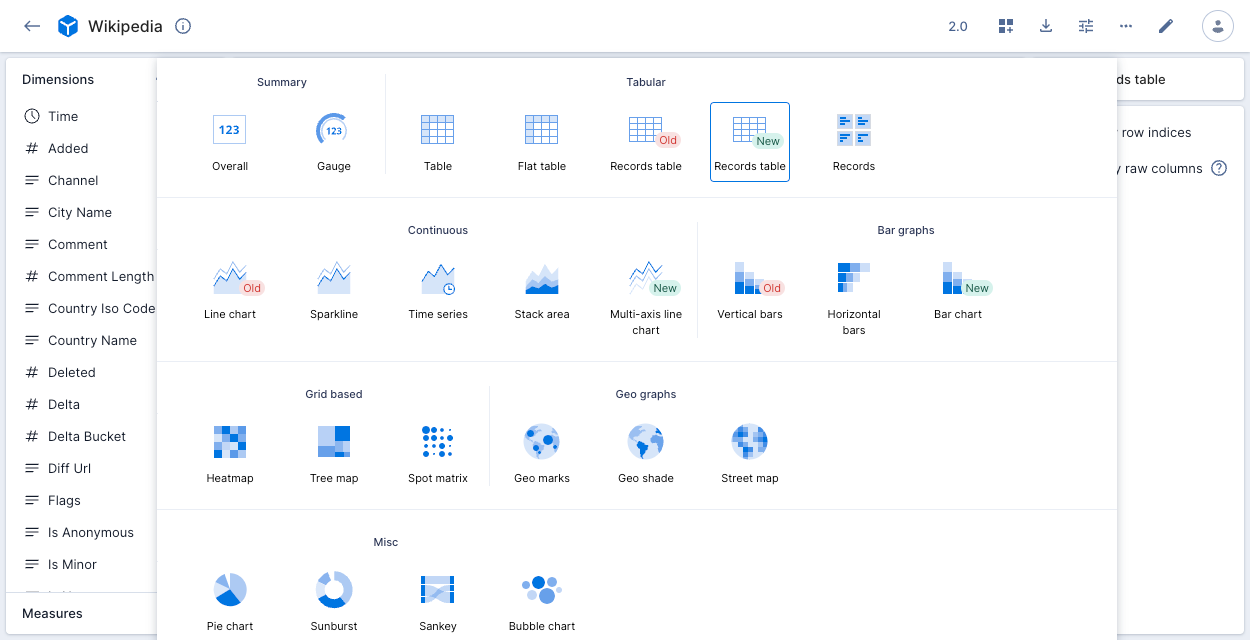
The following sections describe the available visualizations.
Explore visualizations
Explore visualizations are highly configurable and use an Imply variety of SQL for efficient querying of your data. The explore visualizations are:
- Overall (explore) (beta)
- Bar chart (beta)
- Flat table
- Gauge
- Multi-axis line chart (beta)
- Time series
Where two similar visualization are available, for example multi-axis line chart (explore type) and line chart, we recommend using the explore type if it suits your requirements.
Feature flag
Before you can use explore visualizations, you must enable the SDK based visualizations feature flag with the appropriate visualization types in the array. The strings to include in the array for each explore visualization are:
bar_chartflat_tablegaugeline_chartoverallrecords_tabletime_series
For example, ["bar_chart","flat_table","gauge","line_chart","overall","records_table","time_series"] enables all explore visualizations.
Overall (explore)
The default visualization is the overall visualization. It presents a numeric summary of selected measures with your specified filter criteria.
The overall (explore) visualization is a beta feature. Enable the feature flag to use it. If you don't have the beta visualization enabled, see Overall.
You can use the properties panel to add measures, define a time comparison, add a trend line, and configure conditional formatting.
Conditional formatting
If you create an overall visualization with a single measure, you can apply conditional formatting to color the visualization as an indication of data severity—green for ok, amber for warning, red for critical.
To add conditional formatting, click the paintbrush icon in the visualization pane on the right, then click Add condition. Select the condition to apply to the data and the corresponding formatting. You can create multiple conditions.
You can also create a condition based on a comparison. In the following example, the amber color of the visualization indicates that the absolute change in number of deleted events for the previous hour was more than 5,000:
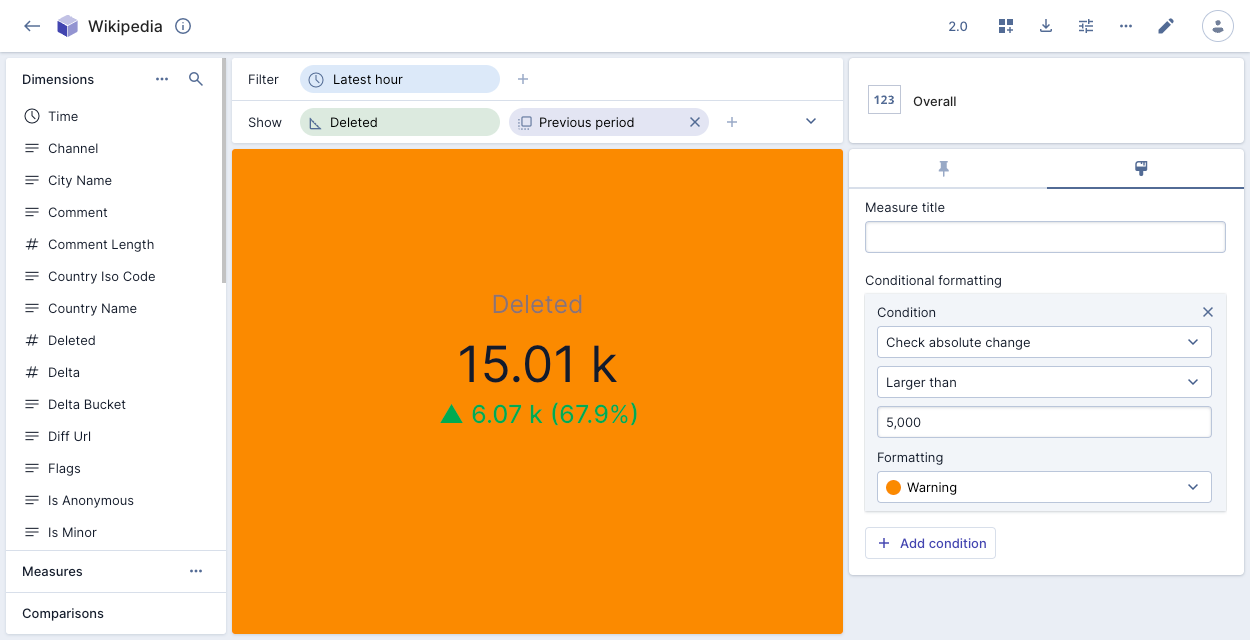
If you add an overall visualization tile with conditional formatting to a dashboard page, the colored icon next to the page name indicates the severity of the data on the page. See Dashboard pages for more information.
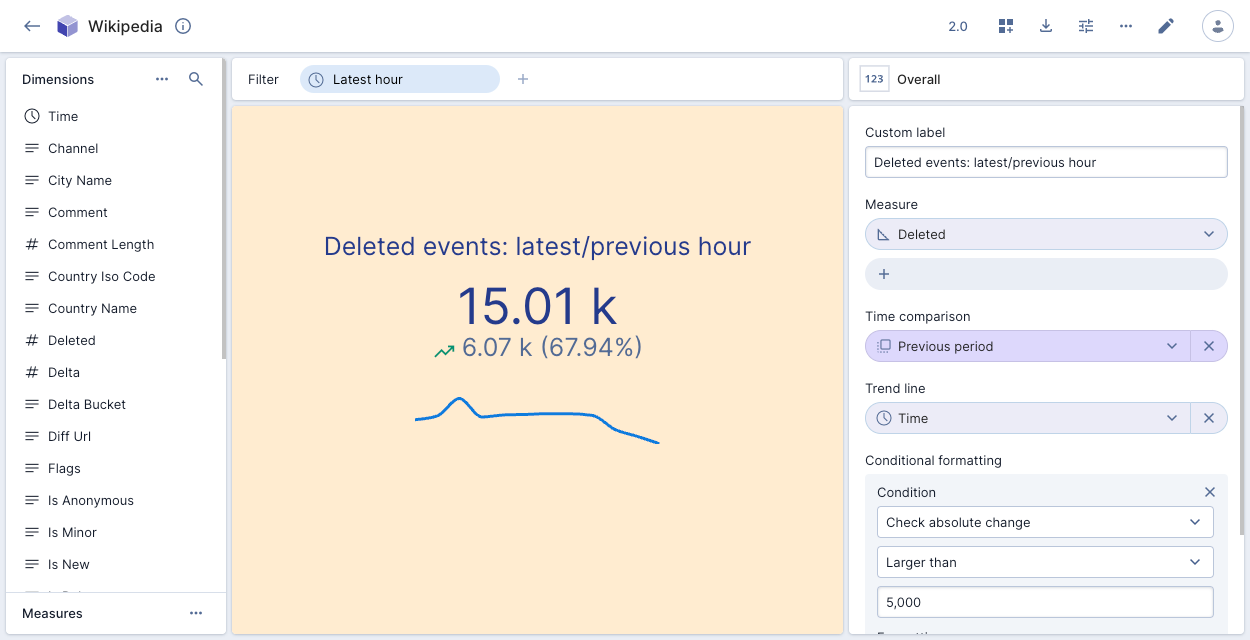
The following example shows the number of events deleted in the latest hour compared to the previous period, with conditional formatting:
Bar chart
The bar chart displays dimensional data as vertical bars.
The overall (explore) visualization is a beta feature. Enable the feature flag to use it. Once enabled, you can continue to access the original vertical bars.
Set the following Fields in the visualization:
- X-axis: Set a column to display on the x-axis. You can limit the number of values to display and sort by measure or dimension.
- Values: Select multiple measures to appear as separate bar charts.
- Stack: Break down the data in the bars across an additional dimension. You can limit the number of stack values and sort by measure or dimension.
- Compare: Time comparison period for the values.
You can also set the following options in the Customizations tab:
- Chart title: Set a title for the bar chart.
- Group series: If you added a Stack dimension, you can group the series horizontally instead of stacking them vertically.
- Show bar values: Show the value of each bar on the chart.
- Legend position: Set the position of the chart legend.
- X axis: Add an x-axis title and select a label orientation.
- Y axes: For each y-axis—add a title, set the decimal precision, set minimum and maximum axis values, select a format (Pivot inherits the format from the measure by default), select a scale type.
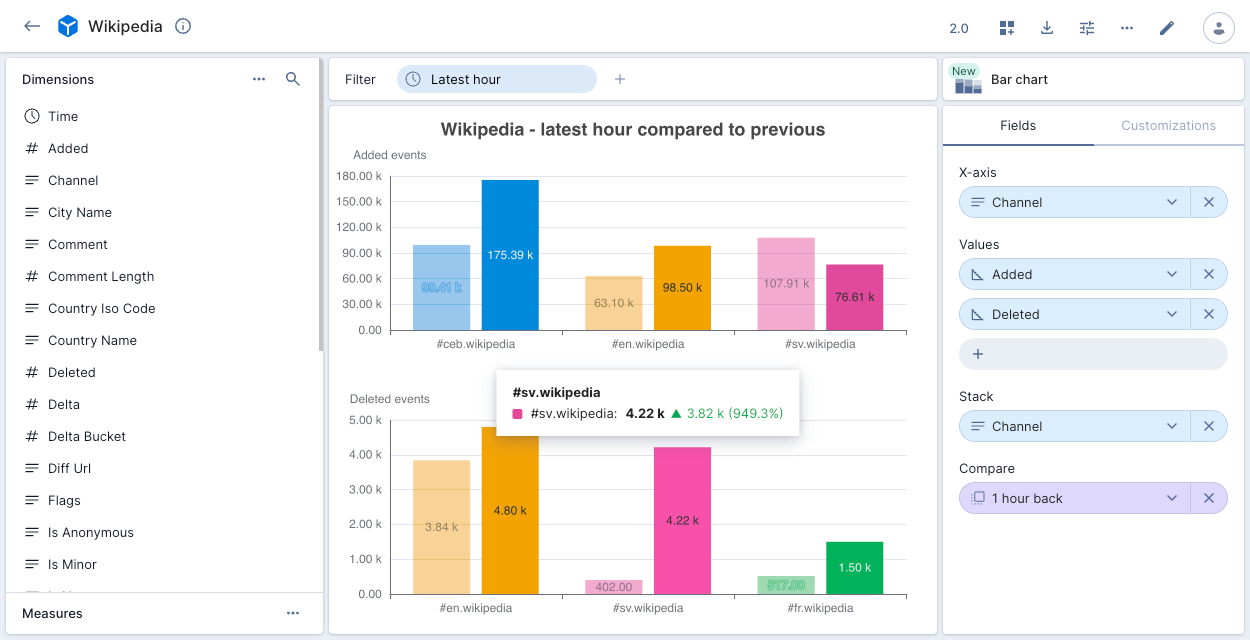
The following example shows three Wikipedia Channel measures with a chart for Added events and a chart for Deleted events. The charts display the number of events for the latest hour compared to the previous hour. Clicking any point on the chart allows you to exclude or filter on the selected data.
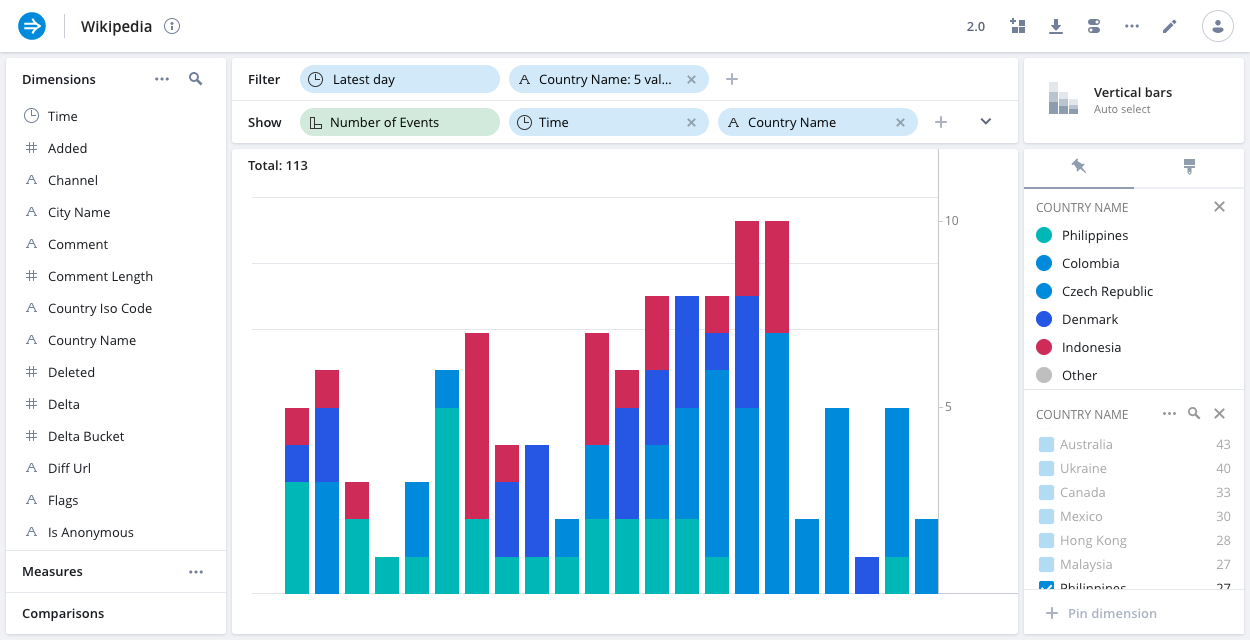
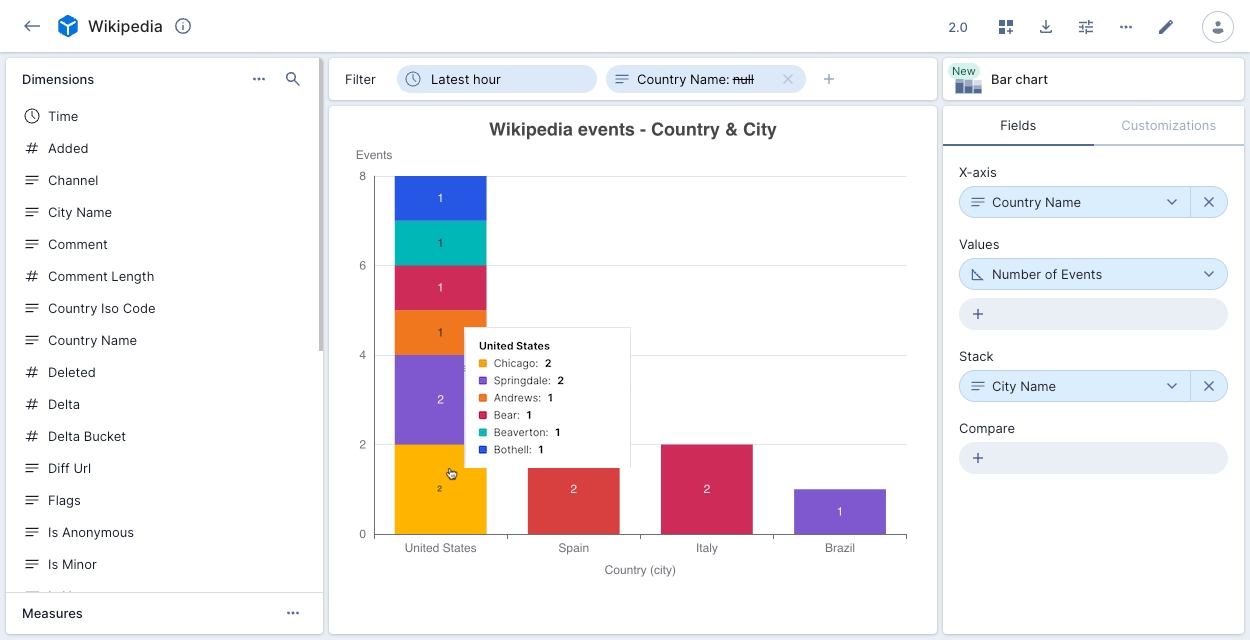
The following example shows Wikipedia events by Country Name, broken down by stack dimension City Name.
Flat table
The flat table visualization is similar to the table visualization but it displays flattened data instead of nested data.
Enable the feature flag to use the flat table visualization.
Select one or more Columns to Group data by and any additional Columns to display.
For columns that contain URLs, hold Cmd (or Ctrl) and click the URL to open it in a new tab.
You can select what to display when a column contains multiple values.
Select a Pivot column and one or more Measures and the visualization displays a column for each combination.
Flat table visualizations translate to queries with GROUP BY on multiple columns. This causes Druid to ignore ranking approximation settings (approximateTopN) even when Exact results only is disabled for the underlying data cube.
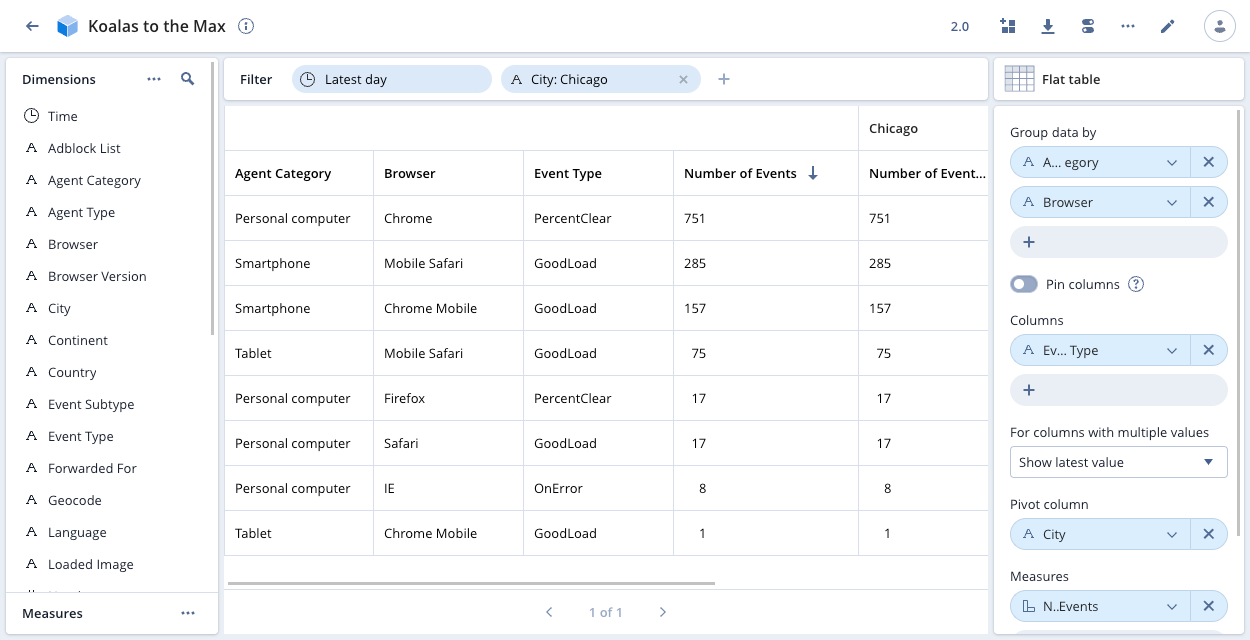
The following example shows the Number of Events for City: Chicago in the Koalas to the Max data cube. The data is grouped by Agent category and Browser. The table shows the additional column Event Type. Where Event type contains multiple values, Pivot displays the latest value.
Gauge
The gauge visualization displays a summary of a selected aggregate as a gauge.
Enable the feature flag to use the gauge visualization.
The gauge shows a number or percentage proportional to the Min and Max values you set. You can color specified ranges, set a custom label, and show a legend.
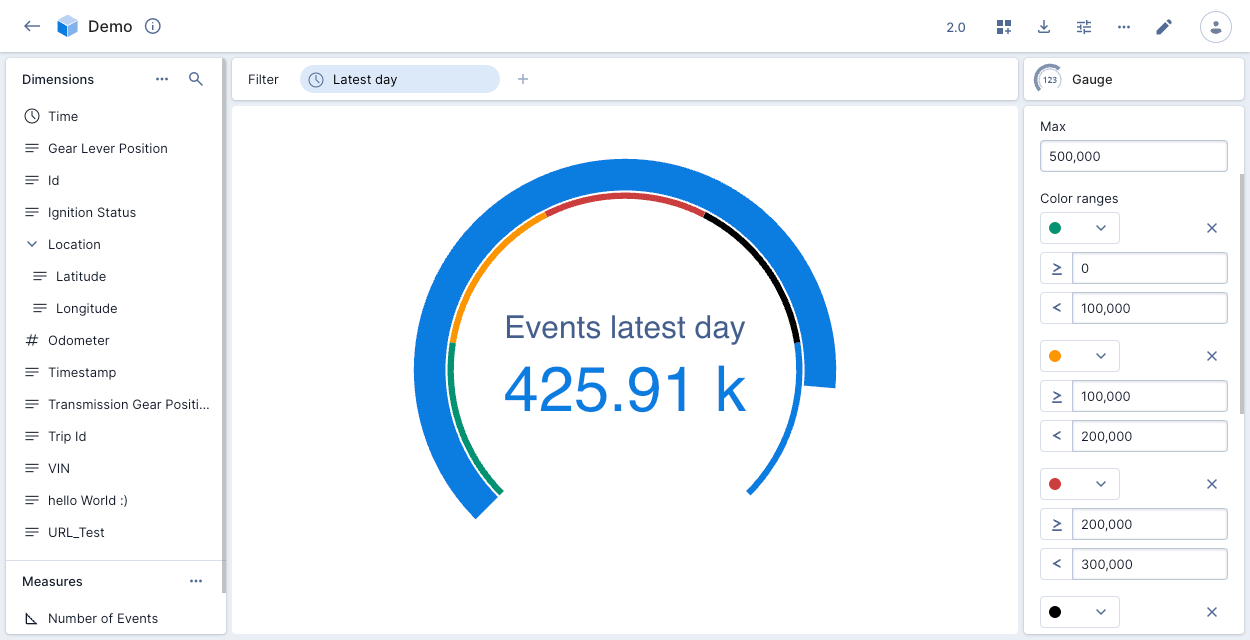
The following example shows the number of events for the latest day in the Demo data cube, proportional to the maximum 500,000. The legend shows four colored numeric ranges.
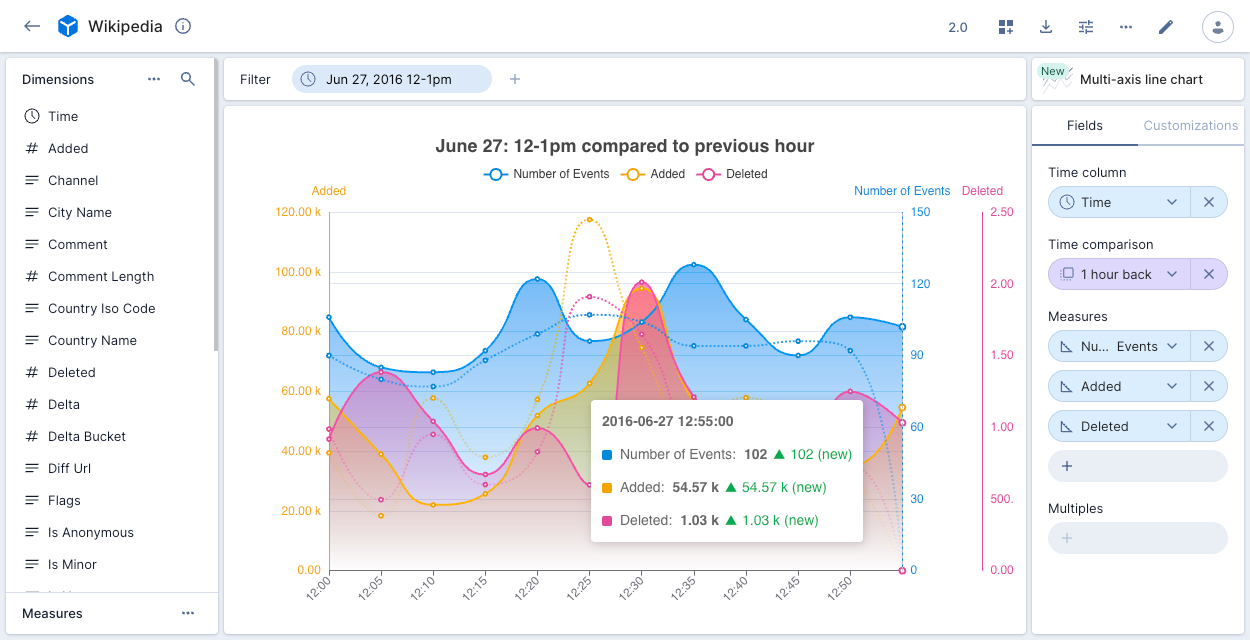
Multi-axis line chart
The multi-axis line chart visualization is designed to demonstrate trends over time.
The multi-axis line chart visualization is a beta feature. Enable the feature flag to use it. Once enabled, you can continue to access the original line chart.
The multi-axis line chart is optimized for the display of multiple axes—you can display up to 10 measures on a single chart. If you want to split the display of multiple measures into multiple charts, use the line chart visualization instead.
Set the following Fields in the visualization:
- Time columns: Time column and bucketing.
- Time comparison: Time comparison period for the measures.
- Measures: Select up to 10 measures to appear on the chart.
- Multiples: Set a multiple to group by a dimension. You can set a limit of up to 10 values, and sort by measure or dimension. Note that you can either show multiple measure or show a groups dimension, not both.
You can also set the following options in the Customizations tab:
- Chart title: Set a title for the line chart.
- Color: Set colors for each line.
- Interpolate: Select how to fill empty values.
- Points: Show or hide data points.
- Line style: Display a smooth, line, or step chart.
- X axis: Add an axis title, select a label orientation, set minimum and maximum axis values.
- Y axis: Label each line, set the precision, set minimum and maximum axis values, select a format (Pivot inherits the format from the measure by default), and scale type.
The following example shows the Number of Events, Added, and Deleted measures for a one hour period in the Wikipedia data cube, compared to the previous hour. A y-axis displays for each measure. Clicking the measure names at the top of the chart adds and removes them from the display. Clicking any point on the chart displays the relevant data.
Records table (explore)
The records table (overall) visualization shows the raw data underlying the data cube, in table format.
The records table (explore) visualization is a beta feature. Enable the feature flag to use it. Once enabled, you can continue to access the original records table.
To use the records table (explore) visualization, click Records table (New) in the visualization selector. You can use the options panel on the right to show the row indices and display columns from the underlying data source instead of the data cube dimensions.
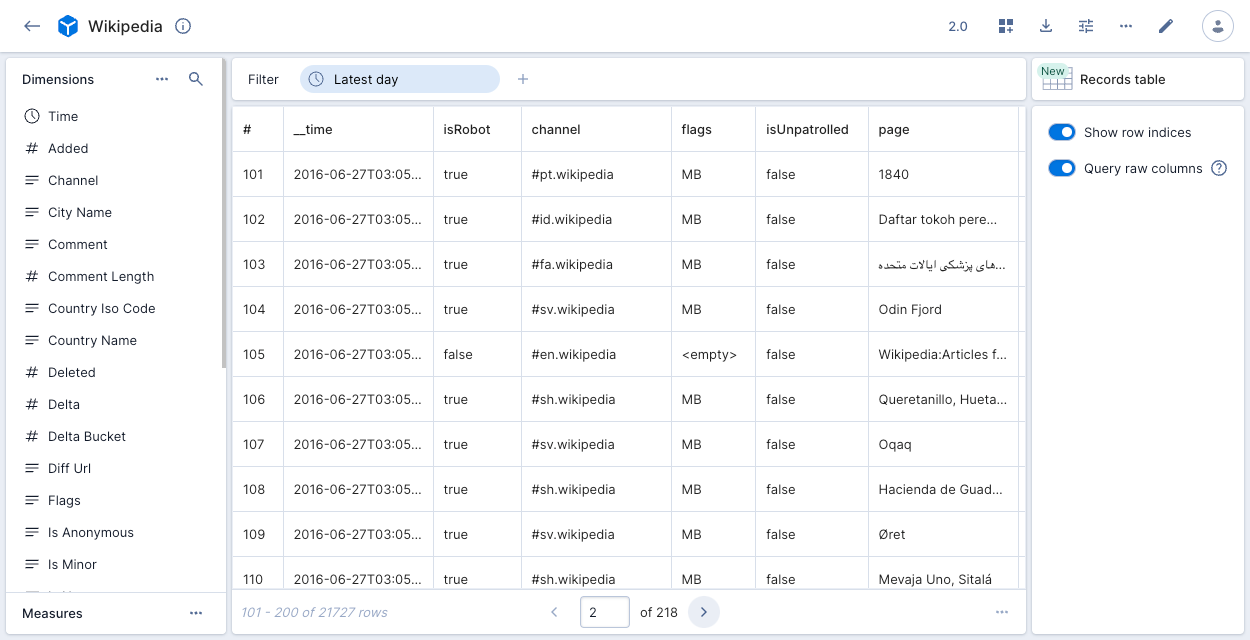
If you want to filter on data in the columns, use the records table visualization instead.
Time series
The time series visualization allows you to use time series functions to generate a line or bar chart showing the rate of change in your data.
Before you can use the time series visualization, you must:
- Load the
imply-timeseriesextension. See Time series functions: Setup for more information. - Enable the feature flag.
Set the following properties in the visualization:
- Render type: Line chart or bar chart.
- Time series function: Select TIMESERIES to create a time series of the data points, or another time series function from the drop-down list.
- Time column: Time column to display on the x-axis.
- Additional Data columns: One or more columns Pivot applies the time series to—the columns Pivot displays depends on the selected function. Data columns display on the y-axis.
- Interpolator: You can specify the method to interpolate missing data points in the time series:
- Linear: Use linear interpolation to fill the missing data points.
- Padding: Carry forward the closest value in the series.
- Backfill: Carry backward the closest value in the series.
- Time series bucket: Choose a segment period for Pivot to use when calculating interpolation points.
- Group by: Column to represent as lines or bars in the visualization.
- Group limit: Limit to apply to the group column.
If Pivot displays a message that the selected window of times contains too many entries to display, adjust the filter to reduce the number of entries.
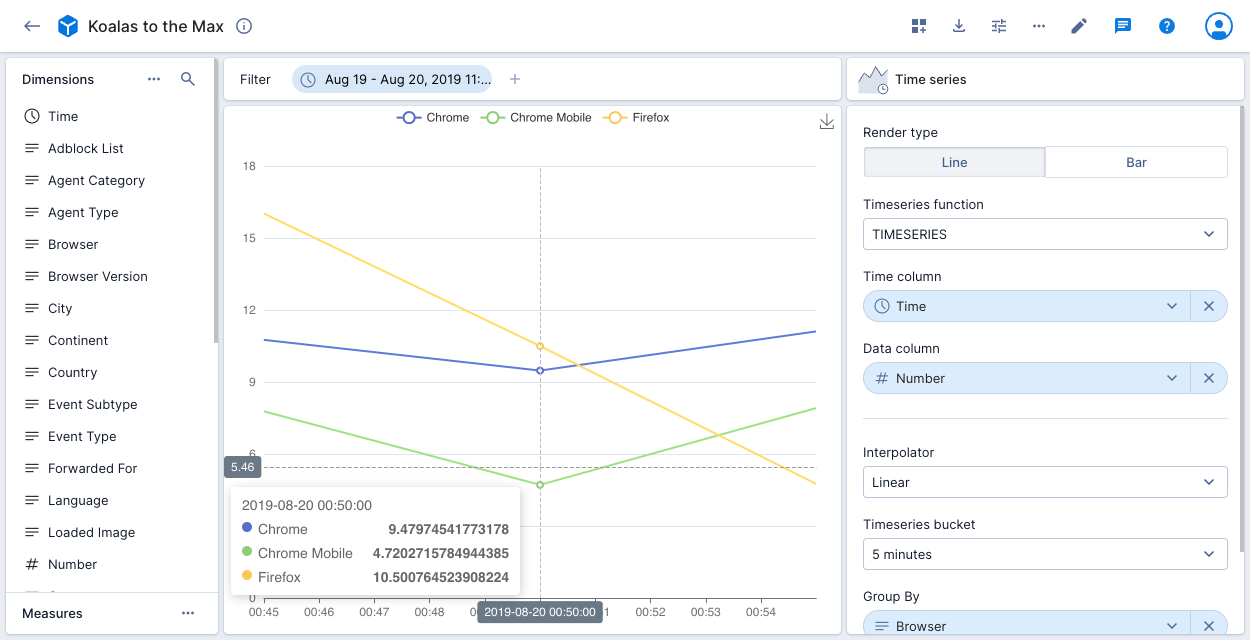
The following example visualization applies the TIMESERIES function to a Koalas to the Max data cube. The data is filtered to a specific period. The time column on the x-axis is Time, with Number shown on the y-axis. The data is grouped by Browser. The visualization displays the top three browsers with the largest number of events. There's a point on the chart for every 5 minutes as set in the time series bucket.
Other visualizations
This section provides descriptions and examples of the visualizations that are not explore type.
Overall
The default visualization is the overall visualization. See Overall (explore) for the explore version of this visualization.
Overall presents a numeric summary of selected measures with your specified filter criteria. You can select multiple measures and show a time range comparison. The following example shows the number of deleted events in the latest hour compared to the previous period:
You can select multiple measures and show a time range comparison. The following example shows the number of deleted events in the latest hour compared to the previous period:
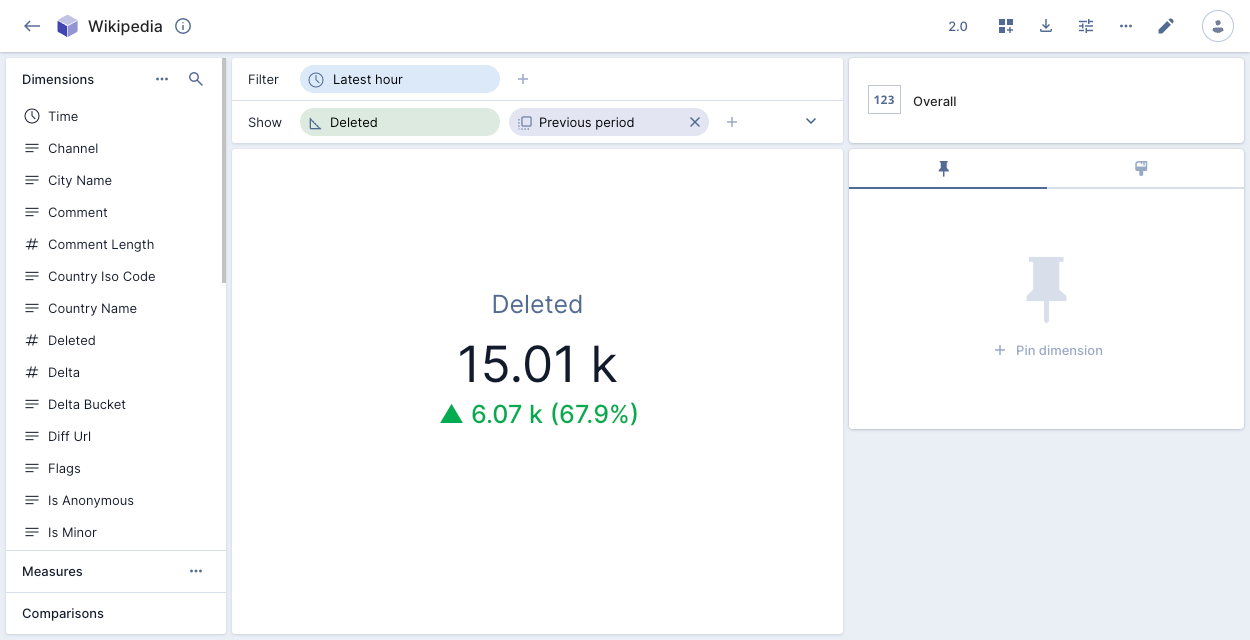
If you create an overall visualization with a single measure, you can apply conditional formatting to color the visualization to indicate data severity.
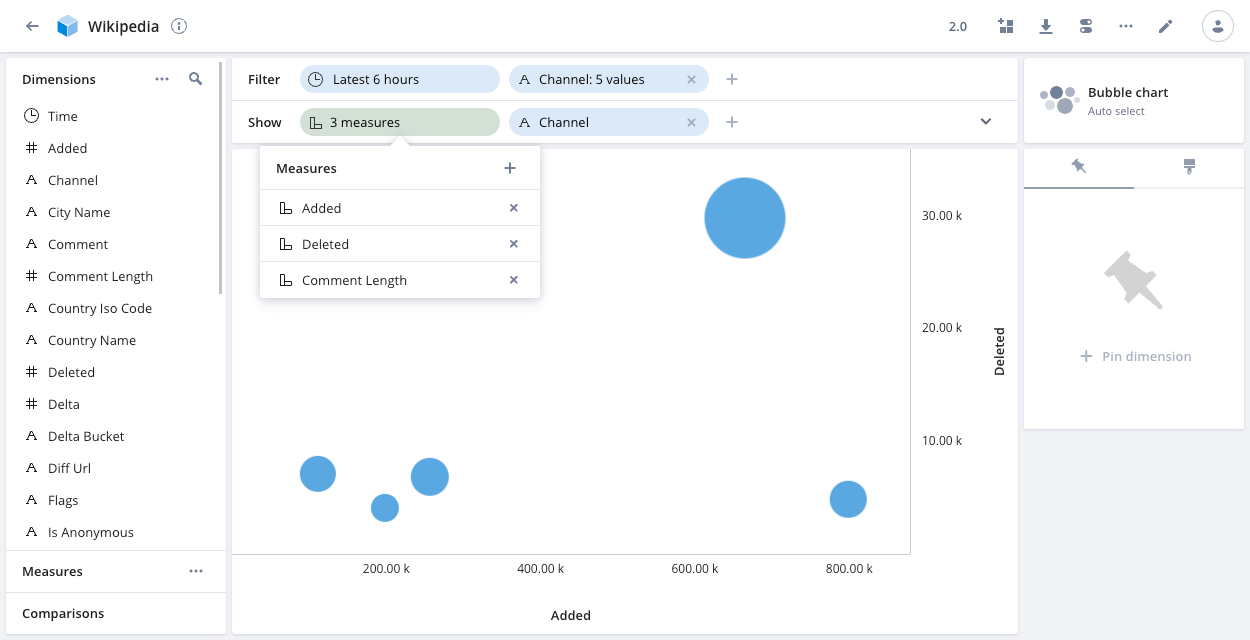
Bubble chart
The bubble chart visualization lets you examine the relationship between two or three numeric variables. Each bubble in the chart corresponds to a single data point, and the measures for each point are indicated by the x-axis (the first measure), the y-axis (the second measure), and bubble size (an optional third measure).
The following example shows a bubble for each of the five channels in the filter. The bubble's horizontal position notes the number of events added to the channel during the latest six hours, and the vertical position notes the number of events deleted from the channel during the same period. The bubble size indicates the relative comment length for the channels.
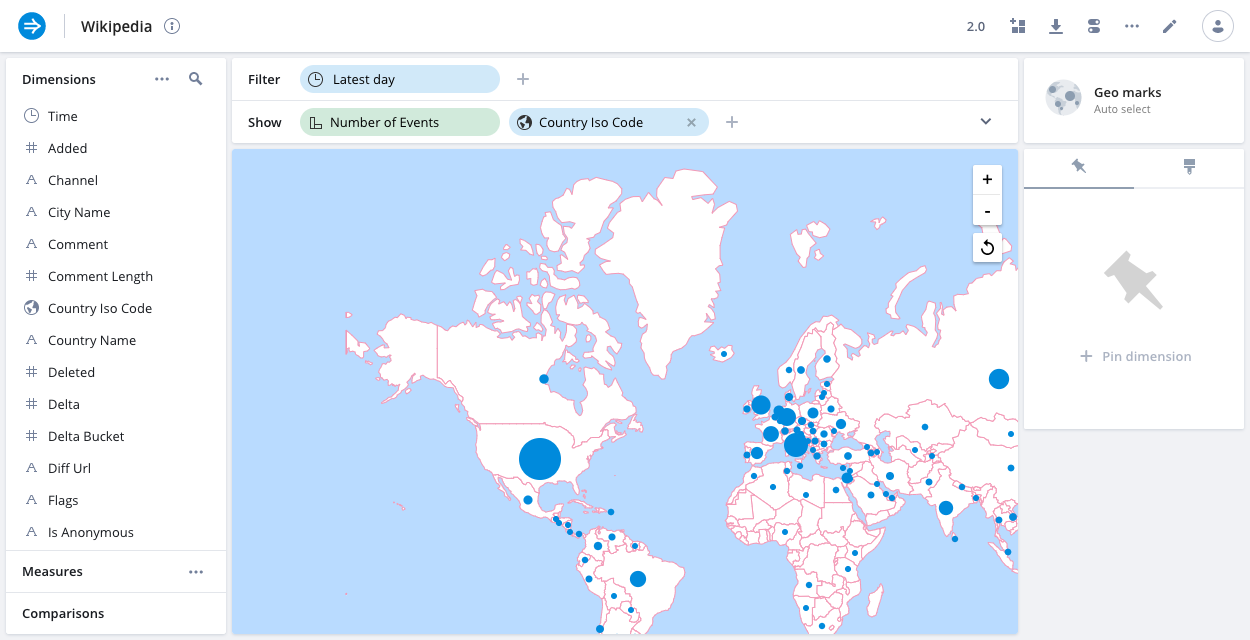
Geo marks
The geo marks visualization is the natural choice for dimensions that represent geographically encoded data. It can work with country encoded data. To use geo-oriented visualizations, modify the data cube configuration to make the country encoded data to be Geo type.
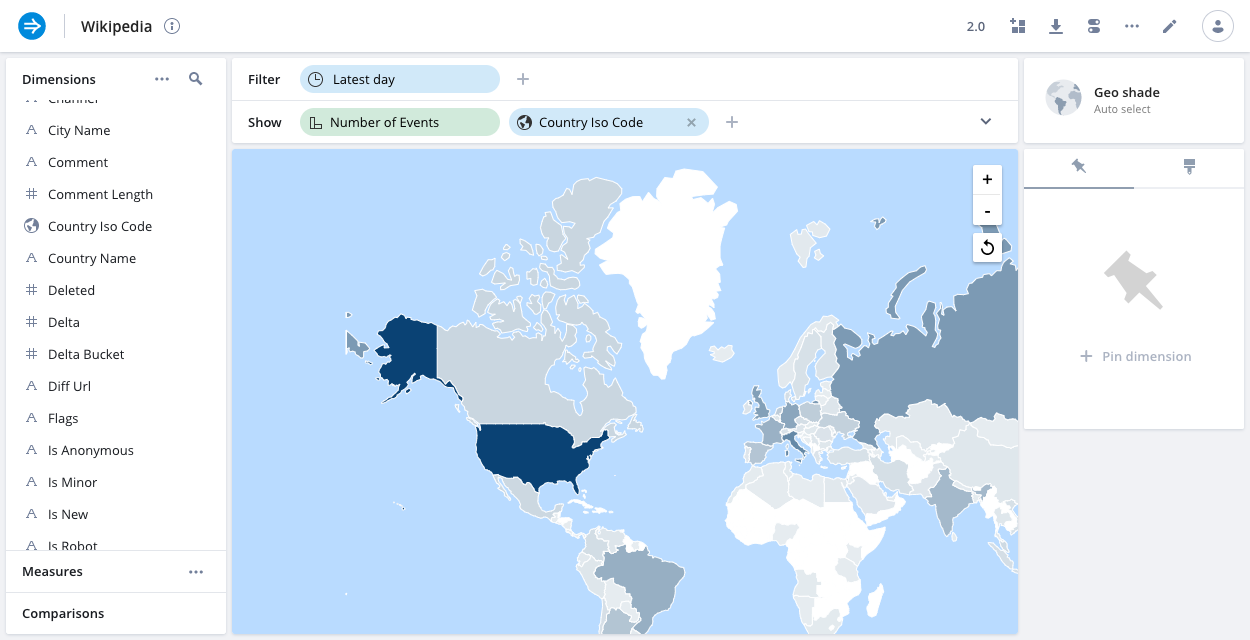
Geo shade
The geo shade visualization (also known as a Choropleth map) is another choice for dimensions that represent geographically encoded data. It can work with country encoded data. To use geo-oriented visualizations, modify the data cube configuration to make the country encoded data to be Geo type.
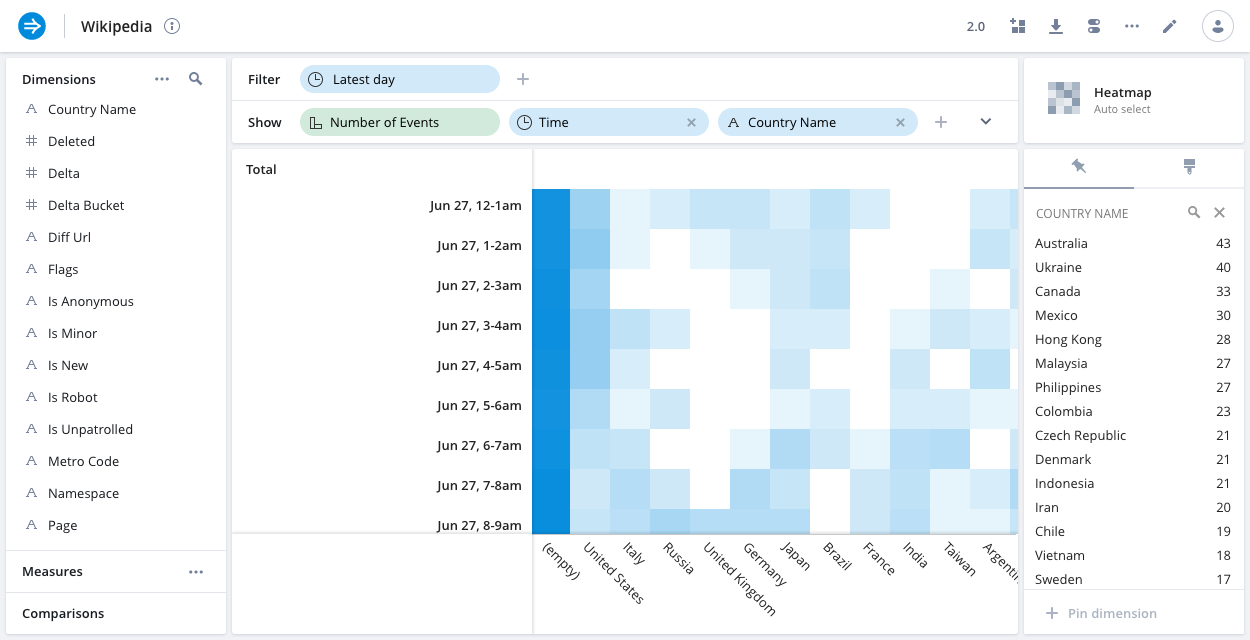
Heatmap
The heatmap is a visualization that shows two dimensions as a 'matrix'. It is similar to the grid visualization and it works particularly well when one or both of the dimensions are continuous.
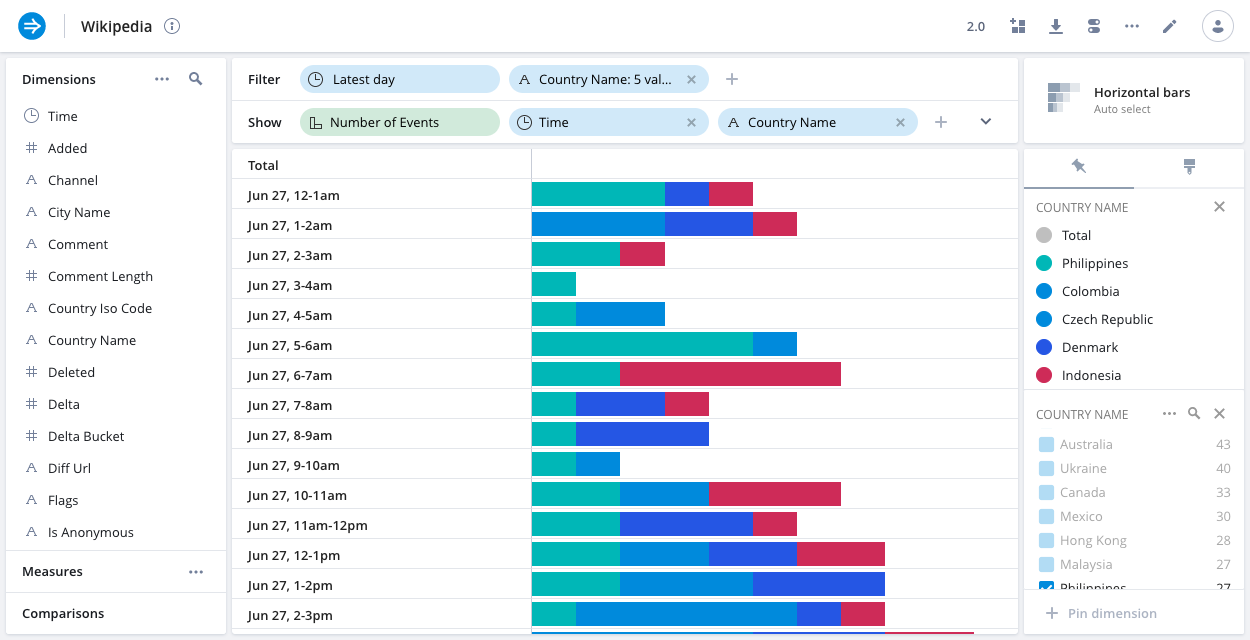
Horizontal bars
The horizontal bars visualization shows each dimension in horizontally oriented time buckets.
Line chart
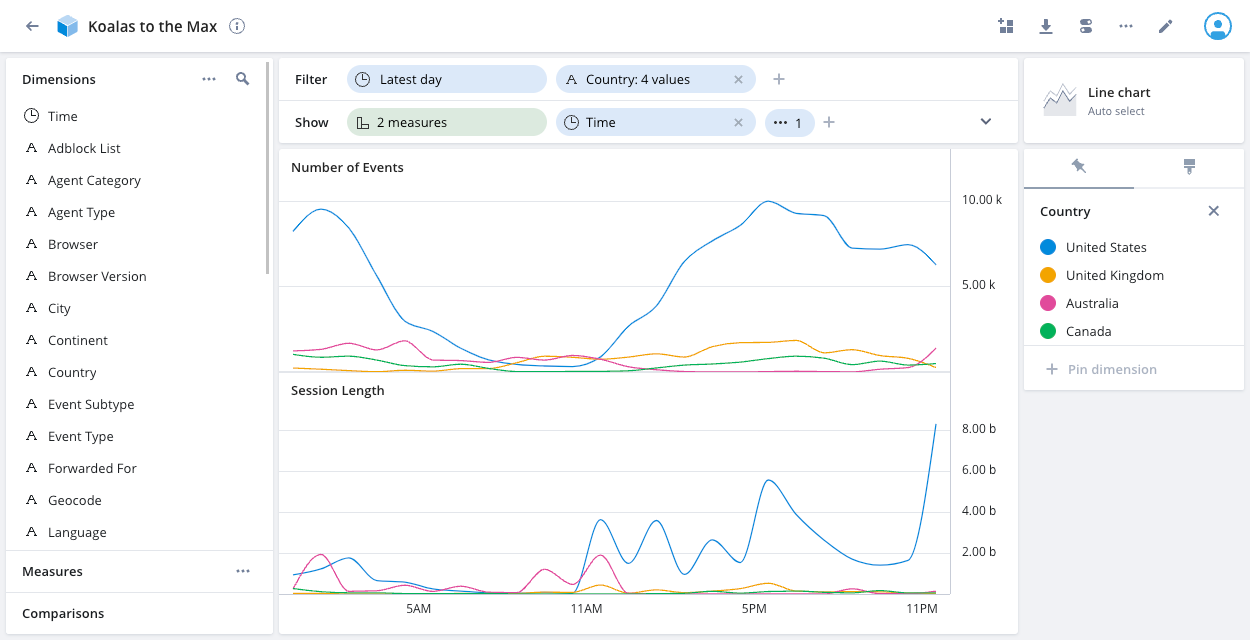
The line chart visualization is designed to demonstrate a trend over time. It's useful for showing temporal dimensions.
Click the paintbrush icon to configure the following options:
- Interpolate: Select how to fill empty values.
- Points: Show or hide data points.
- Horizontal scale: Select Scroll (default) or Fit to view. To display all data in the visible line chart without scrolling, select Fit to view.
The following example line chart displays two measures—Number of Events and Session Length—over time for four Country values.
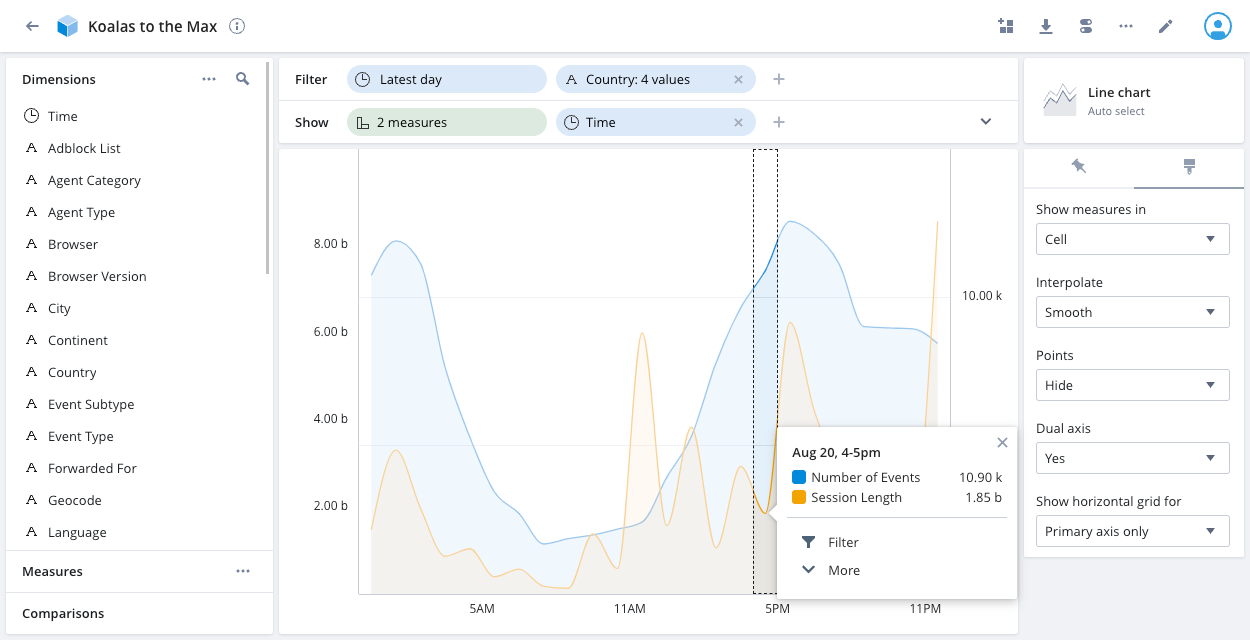
You can display two continuous metrics on the same chart with two axes. To do this, select two measures and then click the paintbrush icon in the right pane. Select Show measures in: Cell and Dual axis: Yes.
The following example line chart displays the same Number of events and Session length measures over time as the above chart. On the dual axis chart, the data for the four selected countries displays as a single line for each measure.
Markdown
You can use a Markdown tile to add formatted text to a dashboard. For more information, see Managing dashboards.
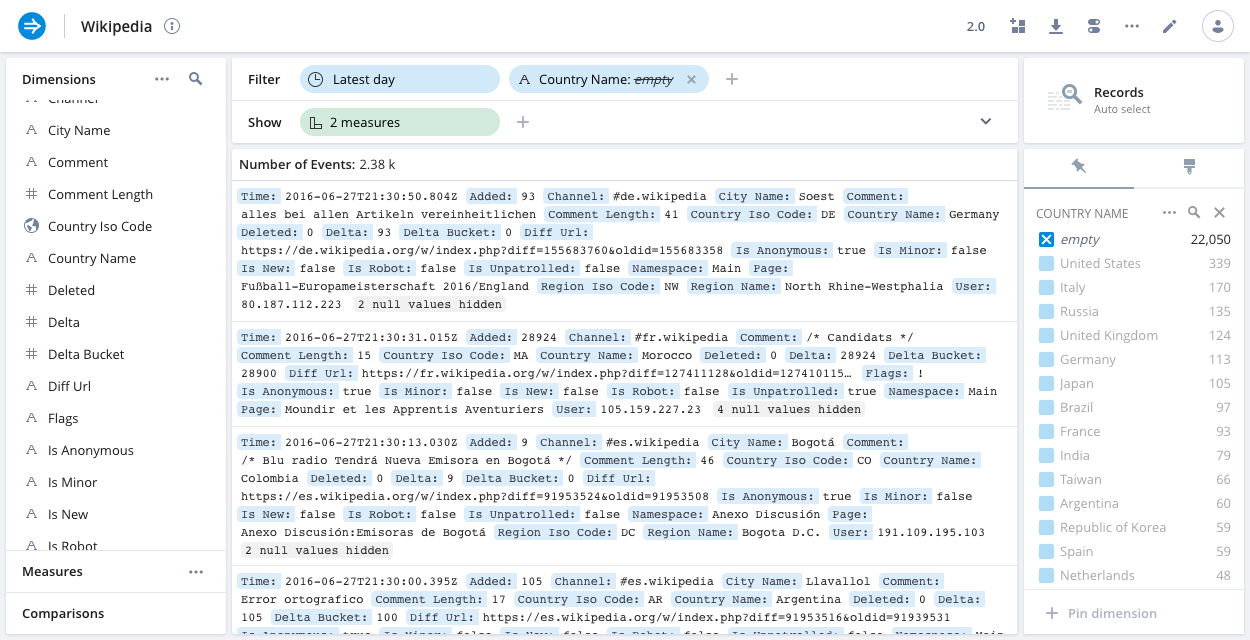
Records
The records visualization shows the raw data underlying the data cube, allowing you to see all dimensions that are in each record. This view can be useful for certain debugging issues. You can also view your records in groups for specific values of one or more dimensions by adding the dimensions to the show bar.
Records table
The records table visualization shows the raw data underlying the data cube, in table format. See Records table (explore) for the explore version of this visualization.
To use the records table visualization, click Records table (Old) in the visualization selector. Click any value in the table to display a menu with options to filter, exclude, and copy data.
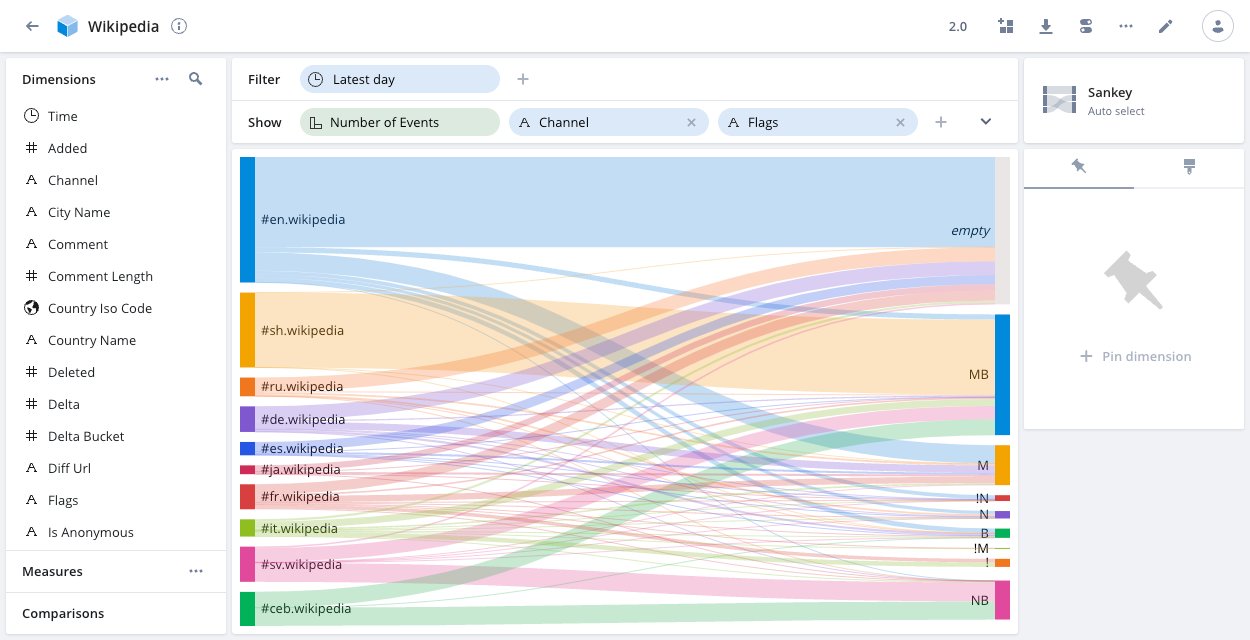
Sankey
The Sankey visualization shows the flow from one set of values to another. In Sankey diagrams, the width of each connection is proportional to the flow volume between the values.
Sparkline
In contrast to the line chart visualization that displays lines for multiple dimensions on a single chart, the sparkline visualization displays multiple line charts—one for each dimension.
The following example sparkline chart displays the number of events over time for five Country Name values:
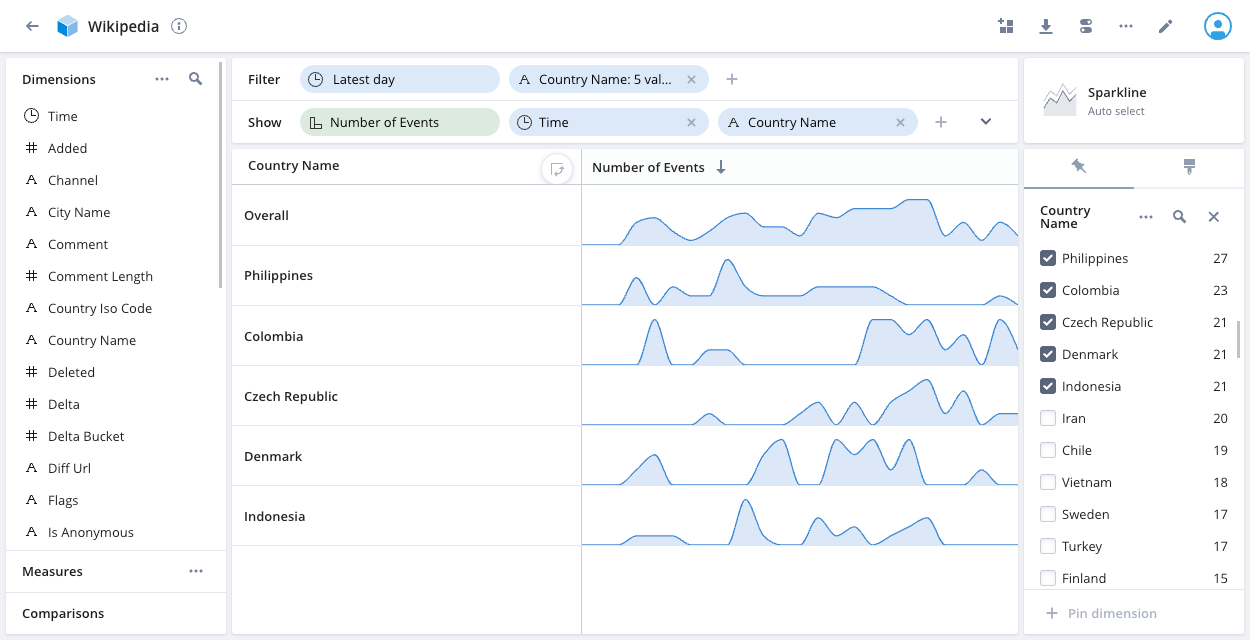
Hover over the first column heading—Country Name in the above example—to display the Swap axes icon. Click the icon to swap the splits assigned to the axes.
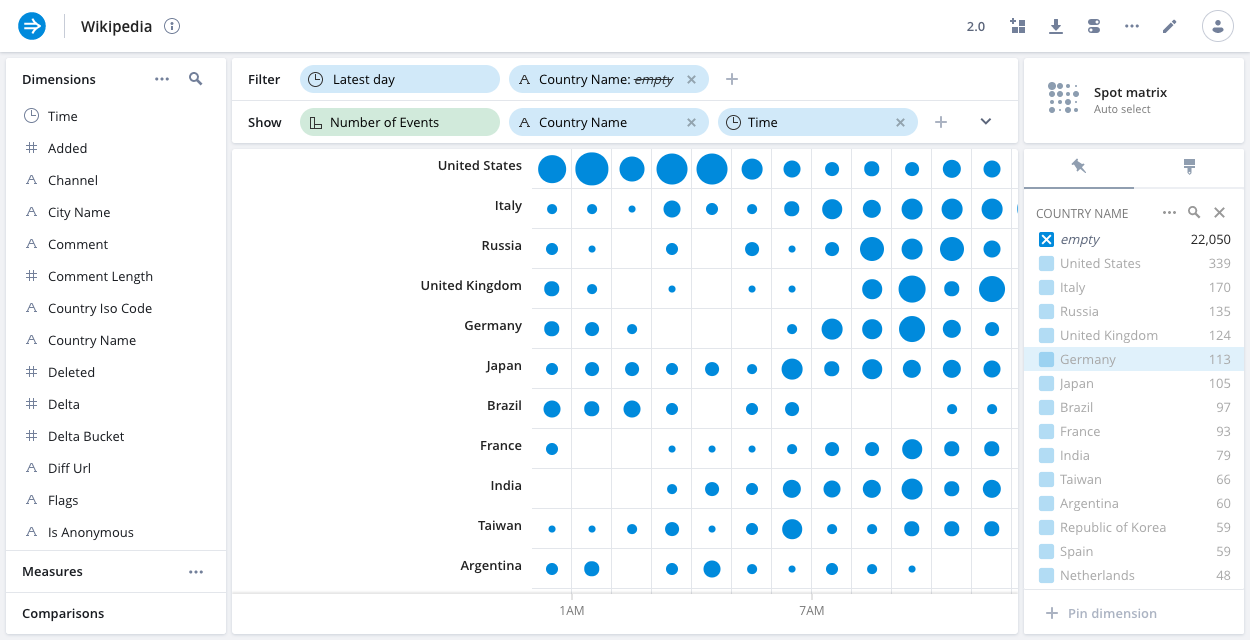
Spot matrix
The spot matrix shows the distribution of events on a two dimensional matrix using circles, with larger circles representing a greater number of events.
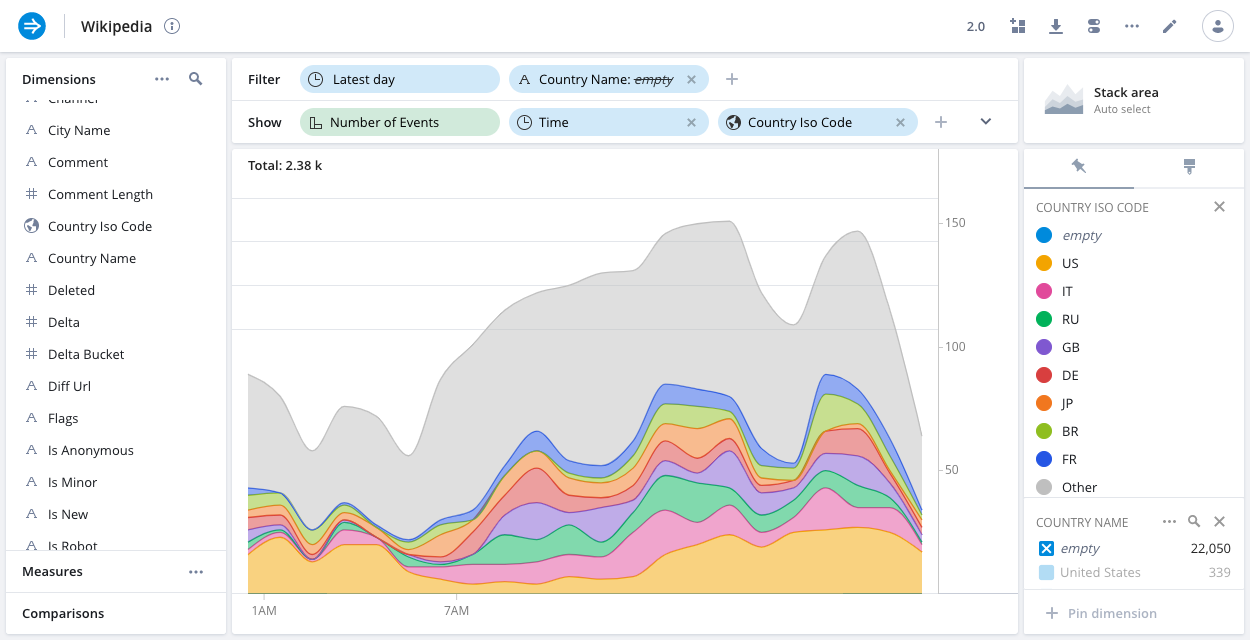
Stack area
The stacked area chart is similar to the line chart, and can be used in similar situations. Unlike the line chart, the area chart lets you see what all the values add up to together. This lets you see the overall trend, while also showing the individual contributions of different dimensions.
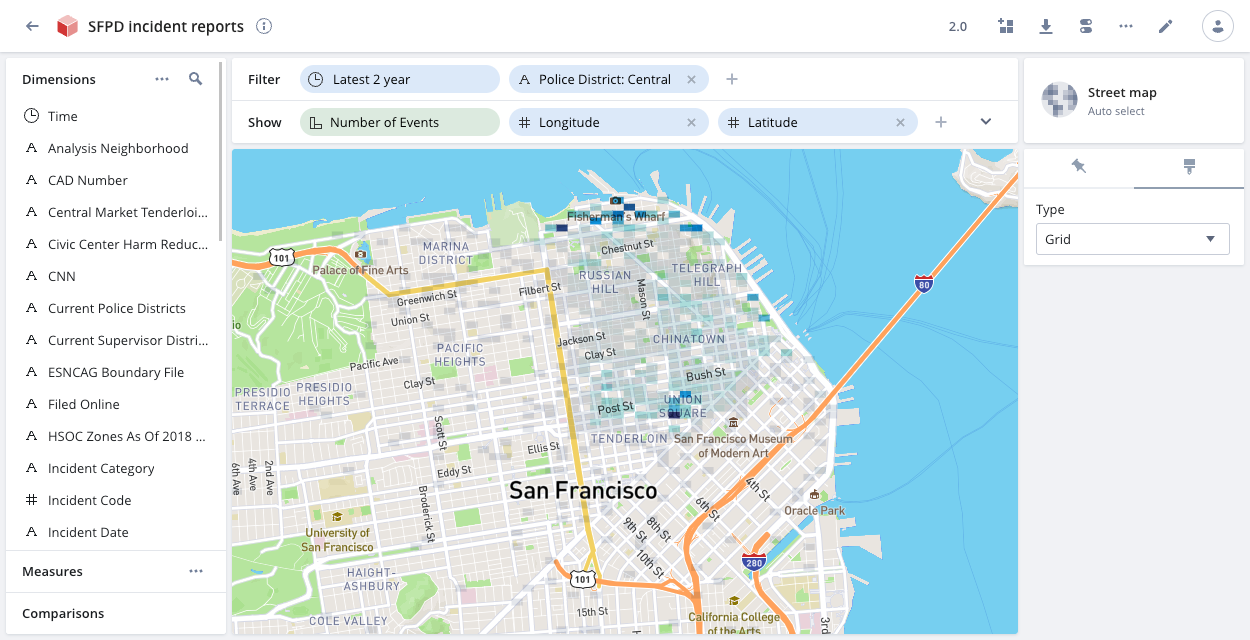
Street map
If your event data contains latitude and longitude coordinates, you can use the street map visualization to pinpoint events to precise locations on a map.
If your Imply deployment is on-prem, contact your Imply support representative to enable the street map visualization.
Create dimensions for your latitude and longitude data. Add the dimensions to the show bar and select Street map from the visualization selector on the right side of the page.
You can click the paintbrush icon to change the default Grid display to Blobs, for a circular representation of the data. The darker the grid or blob color, the higher the concentration of events at that location. Click anywhere in a grid or blob to see the corresponding latitude and longitude coordinates and the number of related events. Click Filter to filter the event display by specific latitude and longitude coordinates.
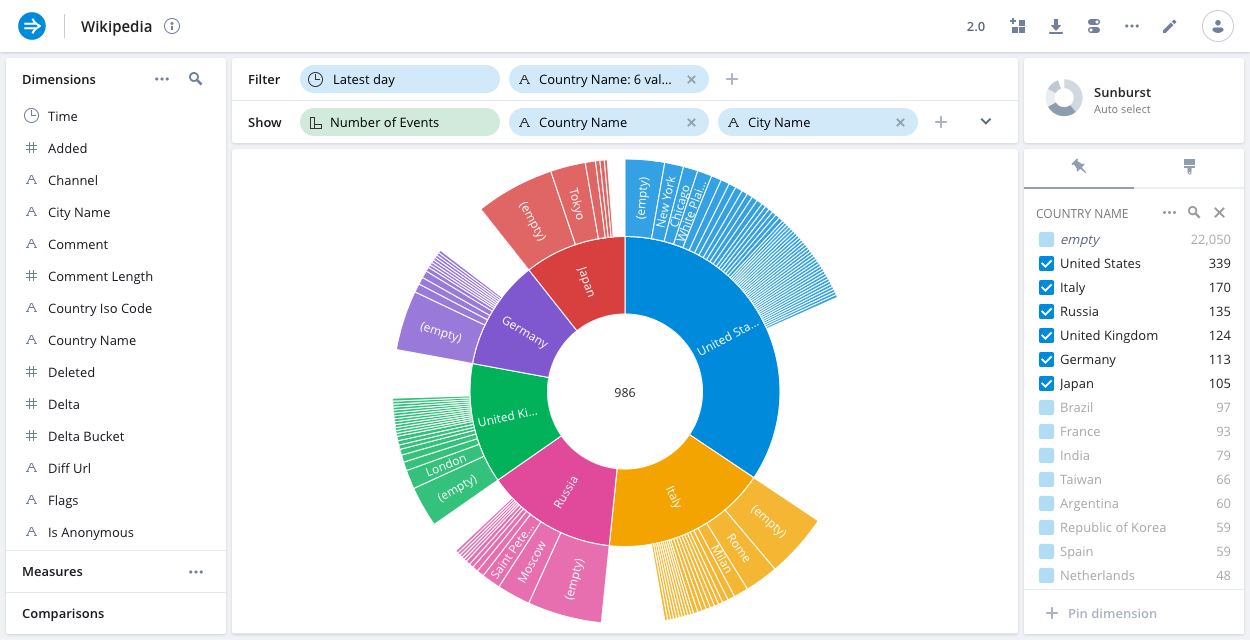
Sunburst
The sunburst (also known as a donut or pie chart when using only one split) is a visualization that represents the ratios between the values of a dimension. When rendering multiple dimensions, each is subdivided to show proportional representation.
Table
The table visualization is the default view for a categorical (string) dimension. It presents a table view of the data with formatting that aids visualization of measure magnitude.
The table visualization can show multiple dimensions, as well as multiple measures, as columns.
For columns that contain URLs, hold Cmd (or Ctrl) and click the URL to open it in a new tab.
The following example shows the number of Wikipedia events for City Name London or New York by Channel for the latest 6 hours, with a comparison to the previous period:
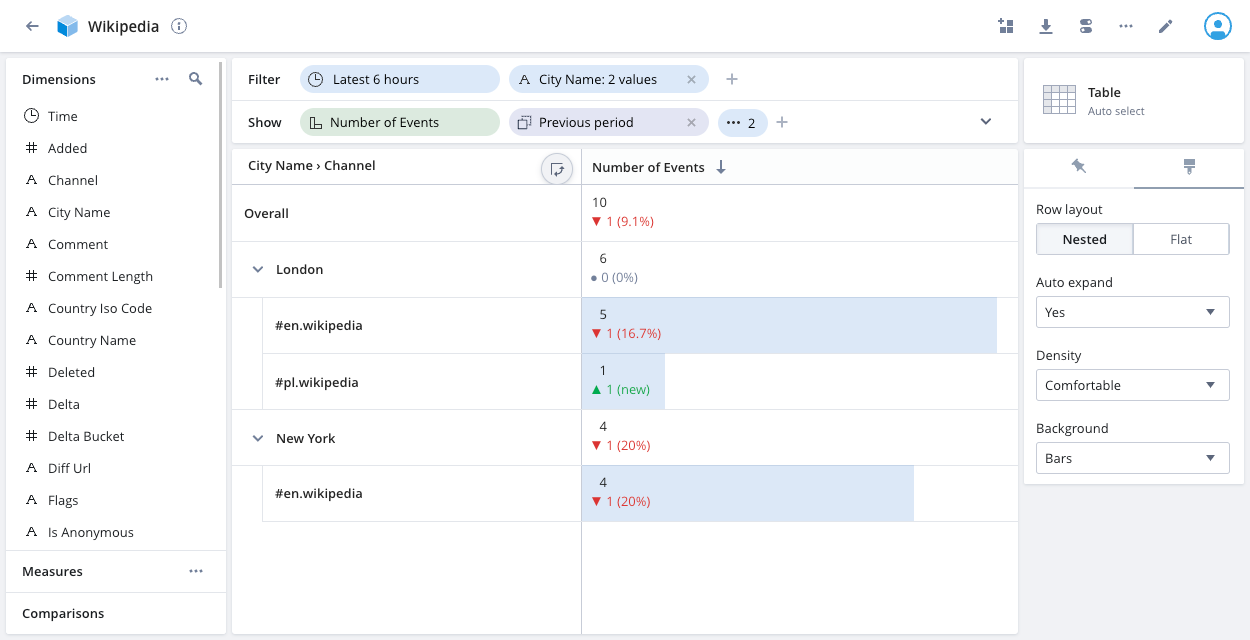
Click the paintbrush icon on the right to access layout options. Pivot displays a nested layout by default—shown above. Click and drag the dimensions in the show bar to rearrange their order and change the nesting.
Hover over the first column heading—City Name > Channel in the above example—to display the Swap axes icon. Click the icon to swap the splits assigned to the axes.
Select the Flat row layout to display a column for each dimension.
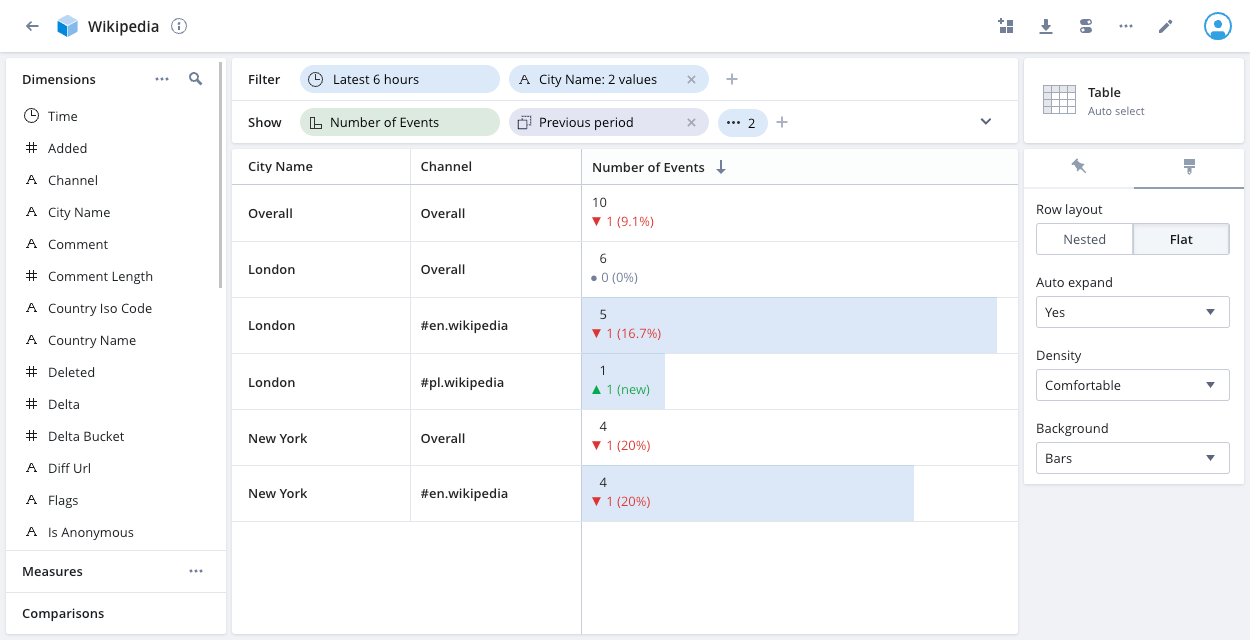
The Overall rows display the dimension totals. In the above example, there are 10 events that match the applied filters—9 for the #en.wikipedia Channel and 1 for #pl.wikipedia. Of the 9 #en.wikipedia events, 5 are for City Name London and 4 are for New York.
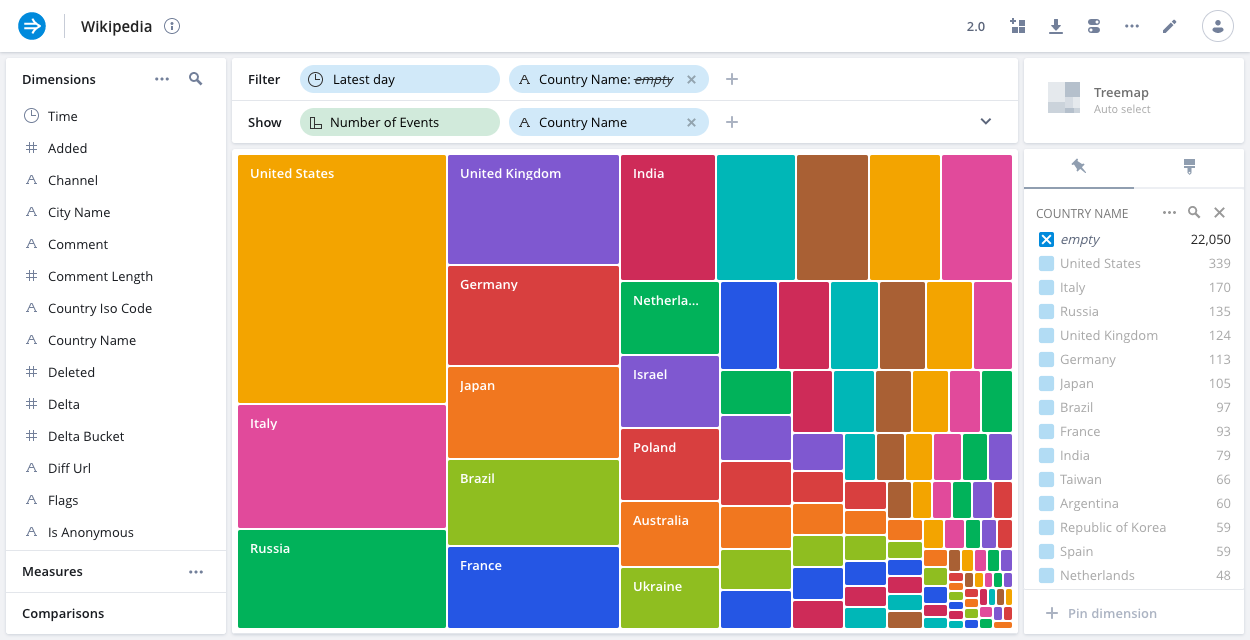
Treemap
The treemap allows you to see how the values of a dimension combine to make up the whole. It is particularly suitable for hierarchical dimensions.
Vertical bars
The vertical bars visualization displays dimensional data as vertical bars. See Bar chart for the explore version of this visualization.